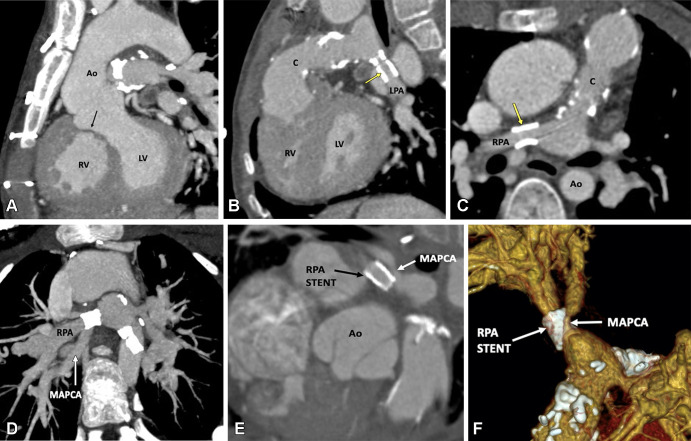
Figure 7:
Postoperative appearance of tetralogy of Fallot with pulmonary atresia after RV-PA conduit (pulmonary homograft) repair, unifocalization of the MAPCAs, and angioplasty of the bilateral pulmonary arteries in a 14-year-old boy. (A) Sagittal oblique maximum intensity projection (MIP) CT image shows a VSD patch (black arrow). (B) Sagittal oblique and (C) axial oblique MIP CT images show RV-PA conduit with multifocal degenerative calcifications in conduit wall. Patent stents are observed in the LPA and RPA (yellow arrow). Stent placement was performed to relieve recurrent branch PA stenosis. (D) Axial oblique MIP CT image shows a stent in the osteoproximal RPA. Another good-sized vessel is observed arising from the RPA which has a unifocalized MAPCA attached to it (white arrow). (E) Sagittal oblique multiplanar reconstruction and (F) volume-rendered images show the origin of the unifocalized MAPCA (white arrow) just proximal to the RPA stent (black arrow in E, white arrow in F). Severe stenosis is noted in the osteoproximal segment of the unifocalized MAPCA. Ao = aorta, C = conduit, LPA = left PA, LV = left ventricle, MAPCA = major aorto-pulmonary collateral arteries, PA = pulmonary artery, RPA = right PA, RV = right ventricle, VSD = ventricular septal defect.