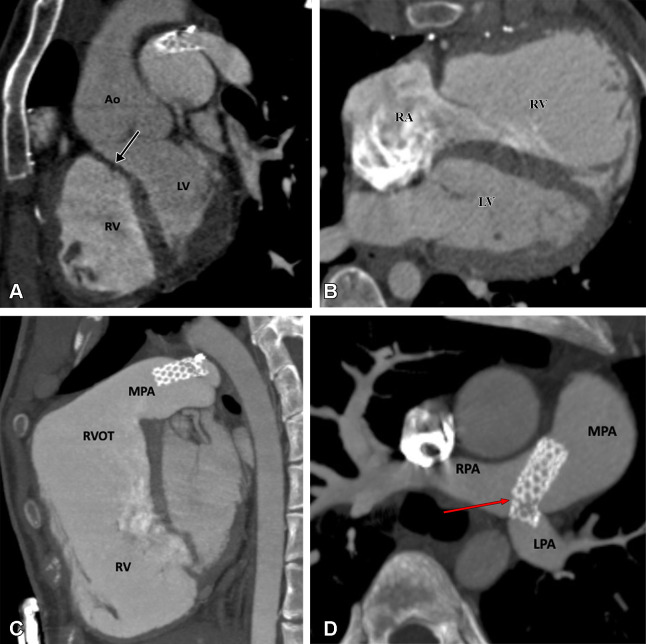
Figure 8:
Postoperative appearance of tetralogy of Fallot after total correction and LPA stent placement in a 17-year-old girl. (A) Sagittal oblique maximum intensity projection (MIP) CT image shows a VSD patch (black arrow). (B) Axial oblique MIP CT image shows grossly dilated RA and RV. (C) Sagittal oblique MIP CT image shows dilated RV and RVOT. A patent stent is seen in the MPA extending into the LPA. Stent placement was performed to relieve recurrent LPA ostial stenosis. (D) Axial oblique MIP CT image shows a patent stent in the distal MPA extending into the LPA. There is proximal migration of the stent with fracture in stent scaffold integrity (red arrow), suggesting stent fracture. Ao = aorta, LPA = left pulmonary artery, LV = left ventricle, MPA = main pulmonary artery, RA = right atrium, RPA = right pulmonary artery, RV = right ventricle, RVOT = right ventricular outflow tract, VSD = ventricular septal defect.