Figure 3. Degradation of IRF2BP2 impairs viability and colony formation in AML and induces apoptosis.
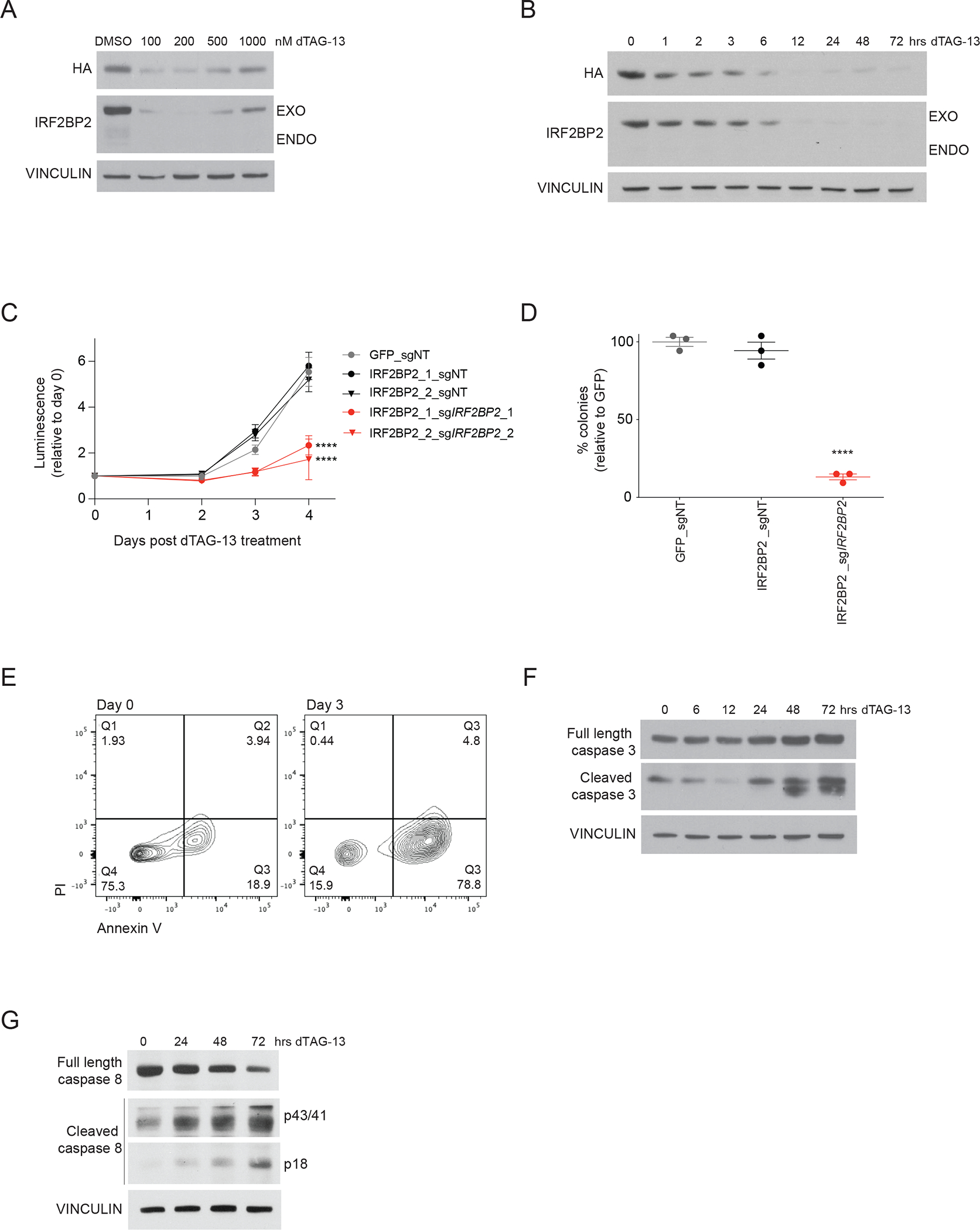
A, Western blot analysis of a dose-response experiment after 24 hours of treatment with dTAG-13 for HA, IRF2BP2 and vinculin in MV4-11 cells with a degradable N-terminally tagged FKBP12F36V-HA-IRF2BP2-fusion and knock-out of endogenous IRF2BP2. A hook effect is observed at the highest concentrations. An HA antibody was used to detect the IRF2BP2-fusion.
B, Western blot analysis of a time-course experiment showing IRF2BP2 protein levels following treatment with dTAG-13 in MV4-11 cells. Vinculin was used as a loading control.
C, CellTiter-Glo viability assay in MV4-11 cells overexpressing a GFP CTRL-ORF or an IRF2BP2 N-dTAG-construct, double-infected with non-targeting (sgNT) or a CRISPR guide targeting endogenous IRF2BP2 (sgIRF2BP2_1, sgIRF2BP2_2) following treatment with 100 nM dTAG-13. Two-way ANOVA, **** p < 0.0001.
D, Colony formation capacity is assessed in MV4-11 cells overexpressing a GFP CTRL-ORF or IRF2BP2 N-dTAG-construct, double-infected with non-targeting (sgNT) or CRISPR guide targeting endogenous IRF2BP2 (sgIRF2BP2) treated with 100 nM dTAG-13 for six days. One-way ANOVA, Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test, **** p < 0.0001.
E, Flow cytometry analysis for Annexin V/PI in MV4-11 cells with degradable IRF2BP2 treated with 100 nM dTAG-13 for 72 hours (right panel) and untreated control cells (left panel).
F, Western blot analysis for full length and cleaved caspase 3 in MV4-11 cells with degradable IRF2BP2 following treatment with dTAG-13 for 0 to 72 hours. Vinculin was used as a loading control.
G, Western blot analysis for full length and cleaved caspase 8 in MV4-11 cells with degradable IRF2BP2 following treatment with dTAG-13 for 0 to 72 hours. Vinculin was used as a loading control.
