Figure 4.
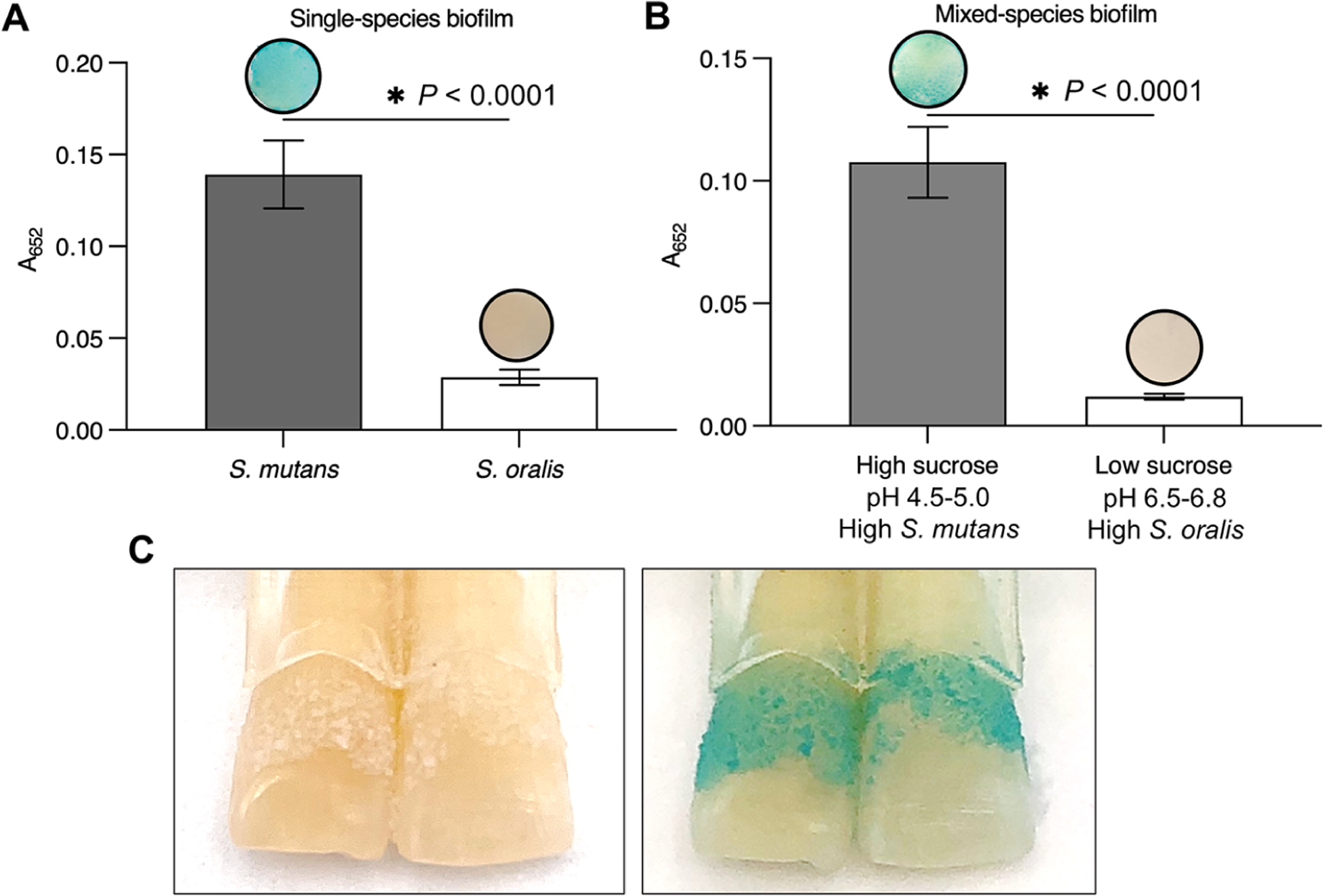
FerIONP detects pathogenic biofilms. (A) S. mutans biofilms were stained in blue by the FerIONP (vs S. oralis biofilms) catalysis of H2O2 via a colorimetric reaction using 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB). For the colorimetric assay, 1% H2O2 was used, which provided an optimal quantitative measurement at an absorbance of 652 nm (as well as clear visualization) within the 5 min reaction time. (B) Similar blue staining was observed in mixed-species biofilms formed with high-sucrose (1%) and a high proportion of S. mutans (>90%) compared to low-sucrose (0.1%) and a low proportion of S. mutans (<10%) (n = 4). Differences between groups were assessed by Student’s t-test. All values are reported as mean ± SD, *P < 0.0001. (C) FerIONP can detect biofilms formed on natural teeth.
