Figure 6. Alveolar myofibroblasts are targets of autonomic innervation.
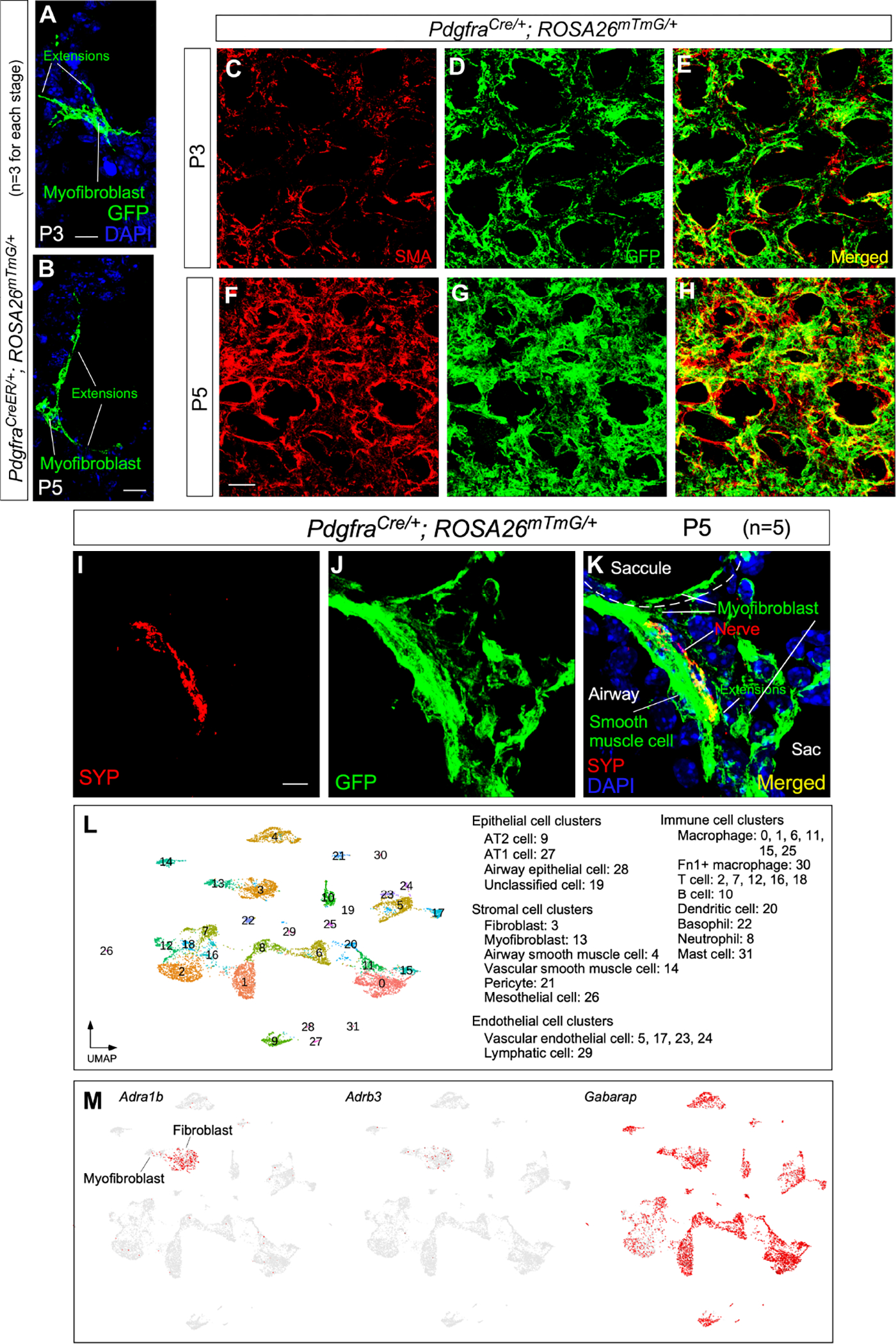
(A, B) Immunofluorescence of lung sections from PdgfraCreER/+; ROSA26mTmG/+ mice (n=3) at P3 and P5 stained with anti-GFP. Leaky expression of Pdgfra-CreER labeled single myofibroblasts with GFP induced from ROSA26mTmG. Myofibroblasts sent out cellular extensions.
(C-H) Immunofluorescence of lung sections from PdgfraCre/+; ROSA26mTmG/+ mice (n=3 for each stage) at P3 and P5 stained with anti-GFP. Myofibroblasts expressed Pdgfra-Cre and were labeled by GFP produced from ROSA26mTmG. Cellular extensions of myofibroblasts were interconnected to form a network, which was apparent by P5.
(I-K) Immunofluorescence of lung sections from PdgfraCre/+; ROSA26mTmG/+ mice (n=5) at P5 stained with anti-GFP and anti-SYP. Nerve fibers (SYP+) could be within 0.1 μm of cellular extensions of myofibroblasts (GFP+) located in saccules.
(L) Single-cell RNA-seq (scRNA-seq) analysis of mouse distal lung cells. Cell clusters of distal lung cells were displayed on UMAP.
(M) UMAP plots of cell clusters that expressed Adra1b, Adrb3 (receptors) and Gabarap across all cell clusters, darker red indicating higher relative expression.
Scale bars, 10 μm (A, B), 25 μm (C-H), 5 μm (I-K).
