Figure 6: Engineered variants efficiently target the central and peripheral nervous system in macaque following systemic delivery.
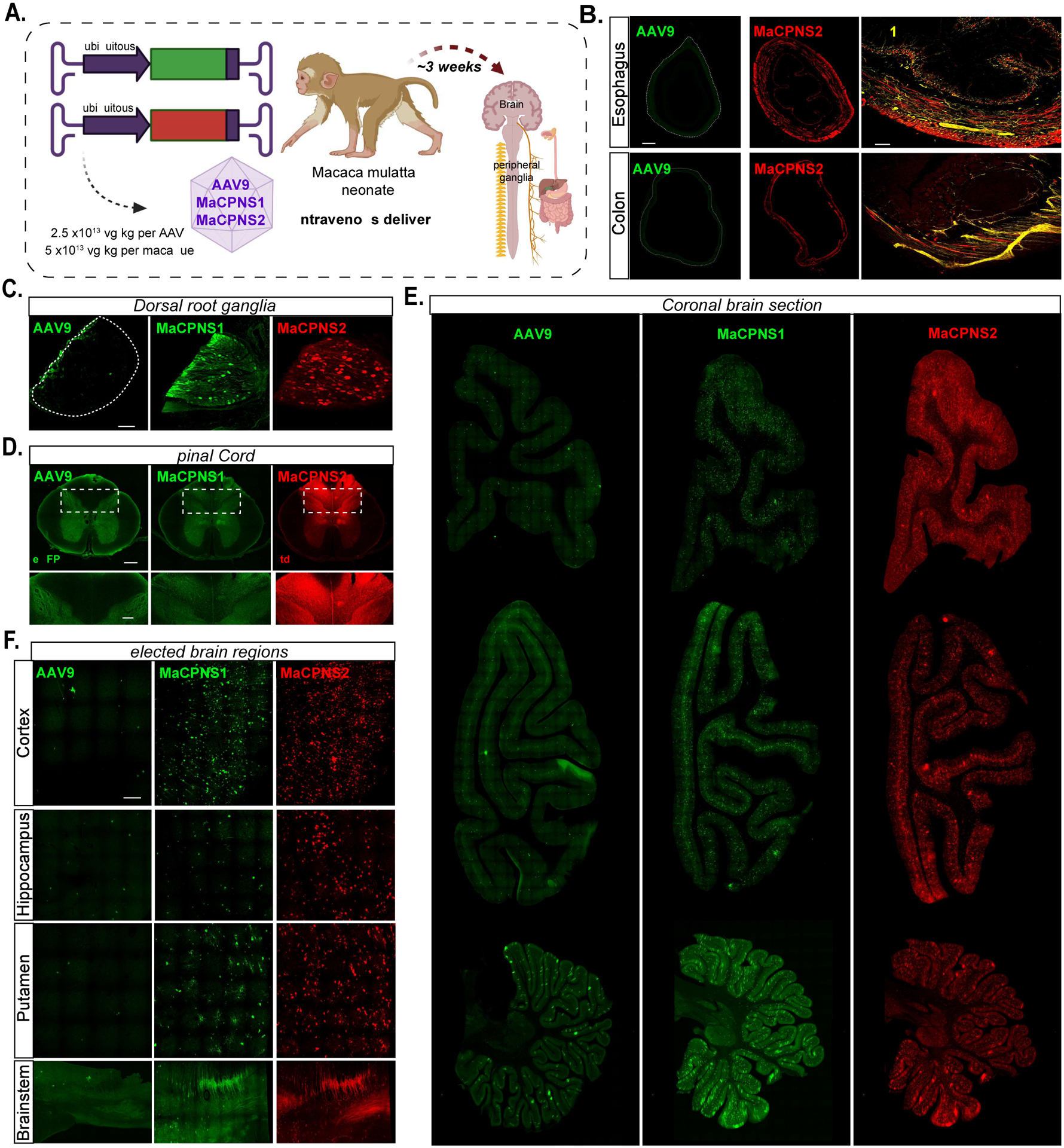
A. Illustration of AAV vector delivery to macaque to study transduction across the CNS and PNS after 4 weeks of expression. The capsids (AAV9/MaCPNS1/MaCPNS2) and their corresponding genomes (ssAAV:CAG-eGFP/tdTomato) are shown on the left. Two AAVs packaged with different fluorescent proteins were mixed and intravenously injected at a dose of 5×1013 vg/kg per macaque (Macaca mulatta, injected within 10 days of birth, female, i.e. 2.5×1013 vg/kg per AAV). Representative images of macaque B., GI regions of esophagus (top panel) and colon (bottom panel) (scale bar: 500 μm, left and 200 μm, right), C., DRGs (scale bar: 200 μm), D., spinal cord (scale bar: 500 μm, top and 200 μm, bottom), E., coronal sections of forebrain, hindbrain and cerebellum (scale bar: 2 mm), and F., selected brain areas: cortex, hippocampus, putamen, and brainstem (scale bar: 200 μm, top and 500 μm, bottom), showing AAV9 vector-mediated expression of eGFP (green), MaCPNS1-mediated expression of eGFP (green) and MaCPNS2-mediated expression of tdTomato (red). The eGFP images of MaCPNS1 are matched in fluorescence intensity to the AAV9 control. The zoomed-in views in B (right panels) show the overlap of MaCPNS2-mediated expression of tdTomato (red) with the neuronal marker Tuj1 (yellow). The zoomed-in views in D (bottom panels) show AAV-mediated expression of eGFP (green) and tdTomato (red) in the fibers in the dorsal column (white dashed boxes).
