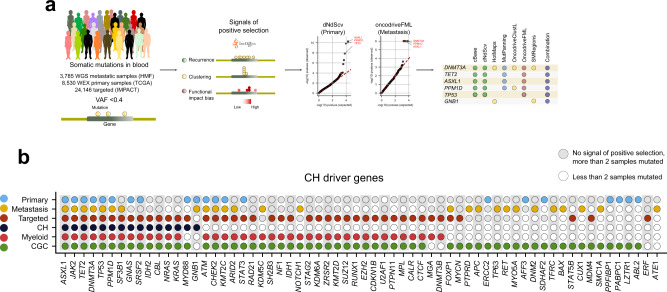
Fig. 2. Discovery of clonal hematopoiesis driver genes.
a Summary of the discovery analysis applied to blood somatic mutations detected across primary, metastasis and targeted cohorts. The (differently filtered) sets of blood somatic mutations identified across all donors of a cohort were the input data for the analysis. Seven state-of-the-art driver discovery methods probing different signals of positive selection were applied (via the IntOGen pipeline) to each dataset of mutations. The distribution of expected and observed p-values (qq plots) for two of these methods (which implement parametric, non-parametric or empirical statistical tests described in the corresponding original articles) are represented in the panel. The IntOGen pipeline also handles the combination of the output of the seven methods to yield a unified list of CH driver genes in each cohort (details in Supp. Note 1). b CH driver genes discovered across the three cohorts. Genes known to be involved in CH, myeloid malignancies or tumorigenesis in general are labeled with different colors (denoted at the left of the plot). The union of the lists of CH drivers discovered in these three cohorts (64 genes) integrate the CH drivers compendium presented in Supplementary Data file 2 and available through www.intogen.org/ch. IMPACT: targeted cohort, CGC cancer gene census. Source data for panel b are provided as Source Data files.