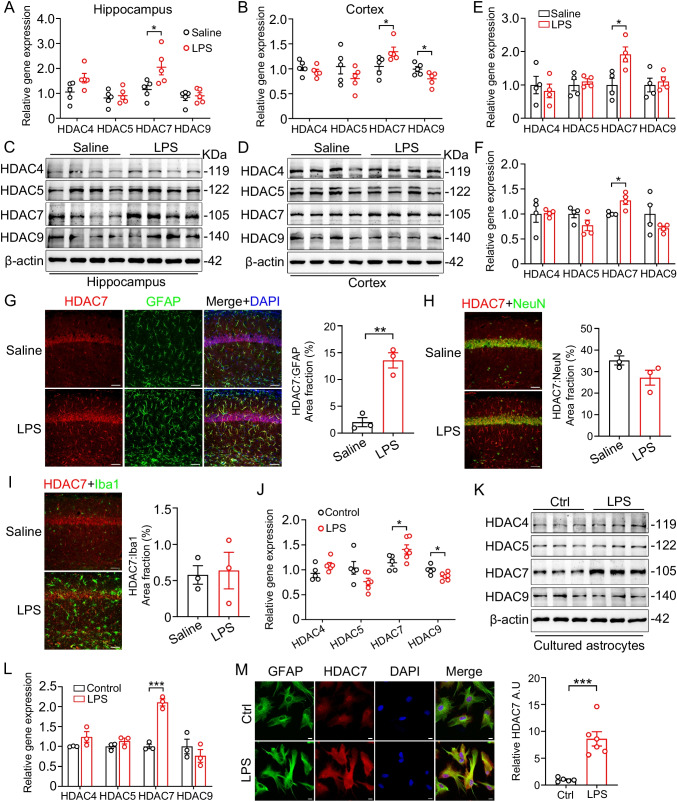
Fig. 1.
HDAC7 level is selectively increased in LPS-stimulated astrocytes in vivo and in vitro. mRNA expression of class IIa HDACs analyzed by RT-qPCR in hippocampus (A) and cortex (B) of LPS- and saline-injected mice (wildtype 2-mon-old C57BL/6 male were intraperitoneally injected with LPS (3 mg/kg) or normal saline and sacrificed 24 h after injection). N = 5 mice for each group, unpaired Student’s t test. Representative western blots of HDAC4, HDAC5, HDAC7, HDAC9, and β-actin in hippocampal (C) and cortical (E) lysates of LPS-treated and control mice. Quantification of HDAC4, HDAC5, HDAC7, and HDAC9 protein levels in hippocampus (D) and cortex (F), β-actin was used as a loading control. N = 4 mice for each group, unpaired Student’s t test. G–I Co-staining of GFAP, NeuN, Iba1, and HDAC7 in the hippocampus after LPS injection. Scale bars, 80 μm. J RT-qPCR analysis of HDAC4, HDAC5, HDAC7, and HDAC9 mRNA expression in primary cultured mouse astrocytes after stimulation with LPS (100 ng/ml) for 24 h. K Representative western blots of HDAC4, HDAC5, HDAC7, HDAC9, and β-actin in LPS-treated primary astrocytes. N = 3 for each group, unpaired Student’s t test. L Quantification analysis of HDAC4, HDAC5, HDAC7, and HDAC9 protein levels normalized to β-actin. N = 3 for each group, unpaired Student’s t test. M Representative immunofluorescence image of GFAP and HDAC7 co-staining in LPS-treated primary astrocytes. Data were expressed as mean ± SEM, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001