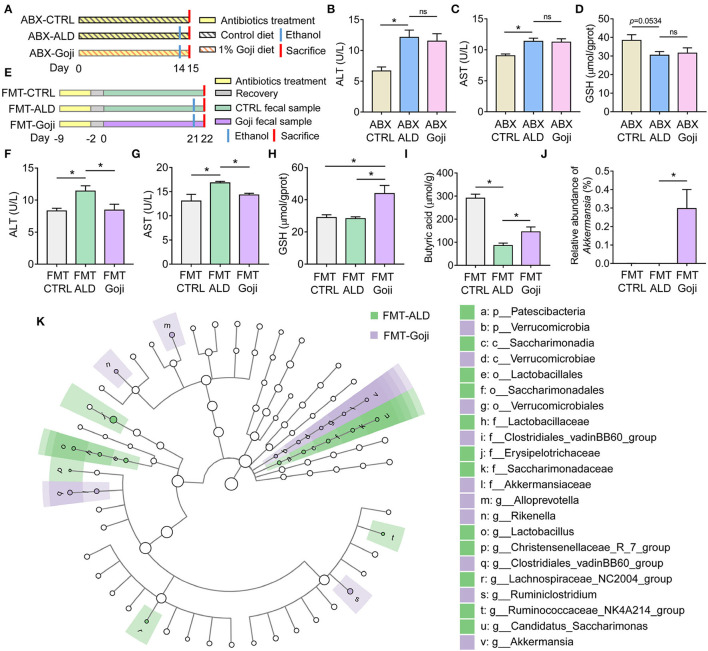
Figure 4.
The liver protective effect of Goji is dependent on gut microbiota. (A) ABX treatment experiment design. (B) the content of ALT in serum. (C) the content of AST in serum. (D) the content of GSH in liver tissue. (E) experiment design. Fecal samples from the CTRL group were transplanted to the pseudo-germ-free mice by antibiotics pretreatment and divided into groups: FMT-CTRL and FMT-ALD. The FMT-Goji group transplanted the fecal samples from the Goji pretreated mice. Both FMT-ALD and FMT-Goji groups were gavaged alcohol to induce alcohol liver injury. (F) the content of AST in serum. (G) the content of AST in serum. (H) the content of GSH in liver tissue. (I) quantification of cecal butyric acid. (J) relative abundance of Akkermansia. (K) significantly different taxa between FMT-ALD and FMT-Goji group analyzed by LEfSe analysis. Data are shown as mean ± SEM, and statistical significance is assessed by one-way ANOVA corrected for multiple comparison by Tukey's test. *p-value < 0.05.