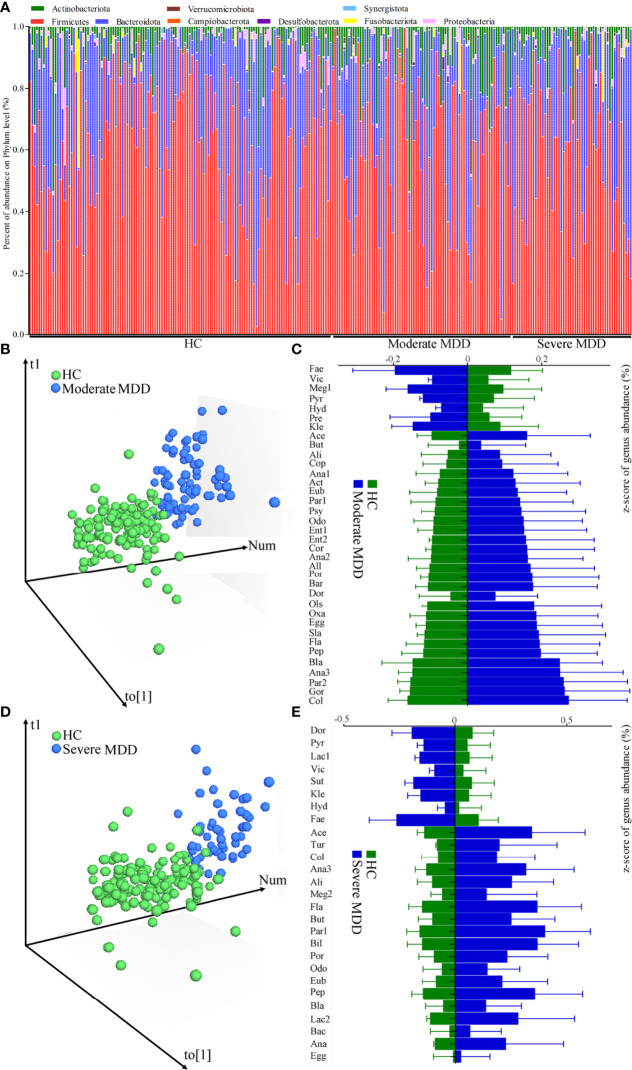
Figure 1.
Changes of gut microbiota compositions in HC and moderate and severe MDD patients. (A) Relative abundances of gut microbiota at the genus level in MDD patients and HC. (B) OPLS-DA model showed that there was only a small overlap between HC and moderate MDD patients, suggesting the divergent microbial changes between the two groups; (C) differential genera responsible for discriminating moderate MDD patients from HC; (D) OPLS-DA model showed that there was only a small overlap between HC and severe MDD patients, suggesting the divergent microbial changes between the two groups; (E) differential genera responsible for discriminating severe MDD patients from HC. HC, healthy controls; MDD, major depressive disorder; Fae, Faecalibacterium; Vic, Victivallis; Meg1, Megamonas; Pyr, Pyramidobacter; Hyd, Hydrogenoanaerobacterium; Pre, Prevotella; Kle, Klebsiella; Ace, Acetanaerobacterium; But, Butyricimonas; Ali, Alistipes; Cop, Coprobacillus; Ana1, Anaerococcus; Act, Actinomyces; Eub, Eubacterium; Par1, Parabacteroides; Psy, Psychrobacter; Odo, Odoribacter; Ent1, Enterococcus; Ent2, Enterorhabdus; Cor, Corynebacterium; Ana2, Anaerofustis; All, Allisonella; Por, Porphyromonas; Bar, Barnesiella; Ols, Olsenella; Dor, Dorea; Oxa, Oxalobacter; Egg, Eggerthella; Sla, Slackia; Fla, Flavonifractor; Pep, Peptoniphilus; Bla, Blautia; Ana3, Anaerotruncus; Par2, Parvimonas; Gor, Gordonibacter; Col, Collinsella; Lac1, Lactococcus; Sut, Sutterella; Tur, Turicibacter; Meg2, Megasphaera; Bil, Bilophila; Lac2, Lactobacillus; Bac, Bacteroides; Ana, Anaeroglobus.