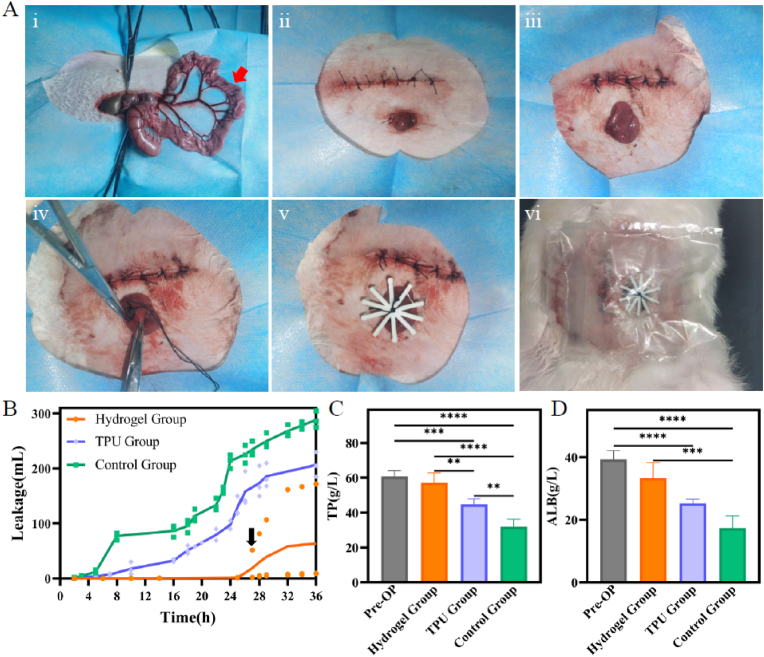
Fig. 8.
Application of 4D-printed bilayer hydrogel in the EAFs of rabbits. (A) Surgical procedure and implantation of 4D-printed bilayer hydrogel stent: (i) Cut open abdomen along linea alba, and pull a section of ileum outside skin through a puncture in the left abdominal wall; Red arrow: surgical stoma location. (ii) Close abdominal wall, and suture the selected ileum to the abdomen; (iii) Cut the exposed ileum via a 2-cm incision to create an EAF model; (iv) Implant a 4D-printed bilayer hydrogel stent; (v) Fix the fistula stent outside abdomen with a 3D printed claw-shaped frame; (vi) Paste on ostomy bags to collect the leaked intestinal juice. (B) Line chart of intestinal juice leakage, black arrow: abscission of the hydrogel stent in one rabbit. (C) Total protein and (D) albumin of pre- and post-operation. ∗∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, statistical analysis using one-way ANOVA.