Extended Data Fig. 4 |. Induced pluripotent stem cell-derived human motor neurons (iPSC-hMN) with SPTLC1 ALS variants.
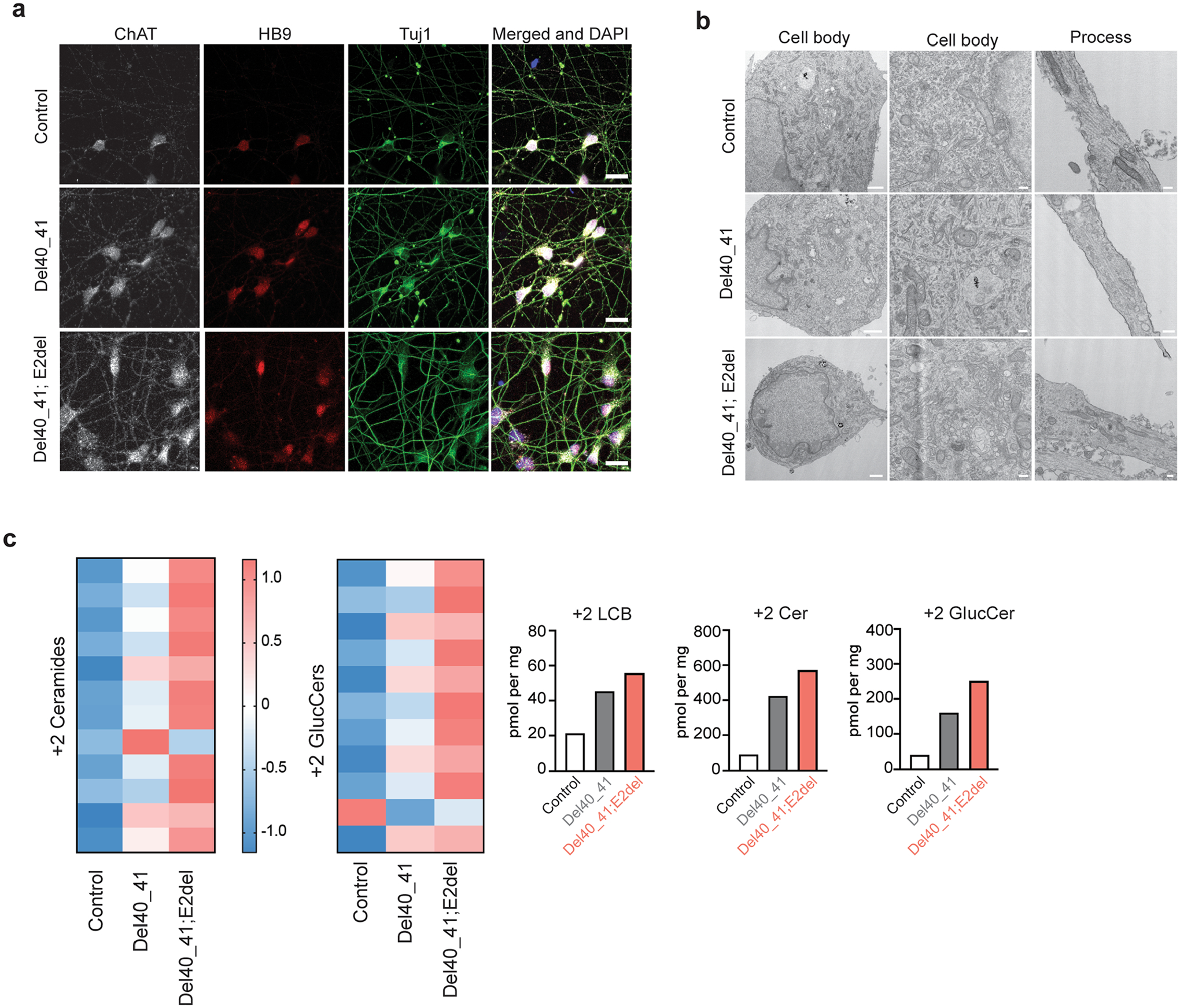
a, After differentiation by addition of doxycycline, SPTLC1 mutant iPSC-hMNs, one with heterozygous SPTLC1 p.F40_S41del variant and the other with compound heterozygous variants SPTLC1 p.F40_S41del; E2del (complete deletion of exon 2) and their isogenic control assume neuronal morphology. They express choline acetyltransferase (ChAT), Hb9 (a motor neuron specific transcription factor) as well as Tuj1 (neuronal microtubule marker). Scale bar = 20 μm b, Electron microscopy of iPSC-hMNs shows normal neuronal cell body morphology, nuclear heterochromatin, and organelles. In the processes (right), microtubules and occasional mitochondria and vesicles are noted. Scale bar left = 1 μm, middle and right = 200 nm. c, Sphingolipidomic analysis of de novo sphingolipid synthesis using isotope labelling (with 3,3-D2 L-serine) depicted in the form a heatmap with each row representing a sphingolipid species. Row Z-scores were calculated and depicted in colour. Canonical sphingolipids ceramides and glucosyl ceramides (glucCer) are increased in p.F40_S41del iPSC-hMNs compared to their isogenic control and increase further in the double mutant iPSC-hMNs. The bar graphs show the increase in total 2+ long-chain bases (LCB), ceramides (Cer), and glucosyl ceramides (GlucCer).
