FIGURE 2.
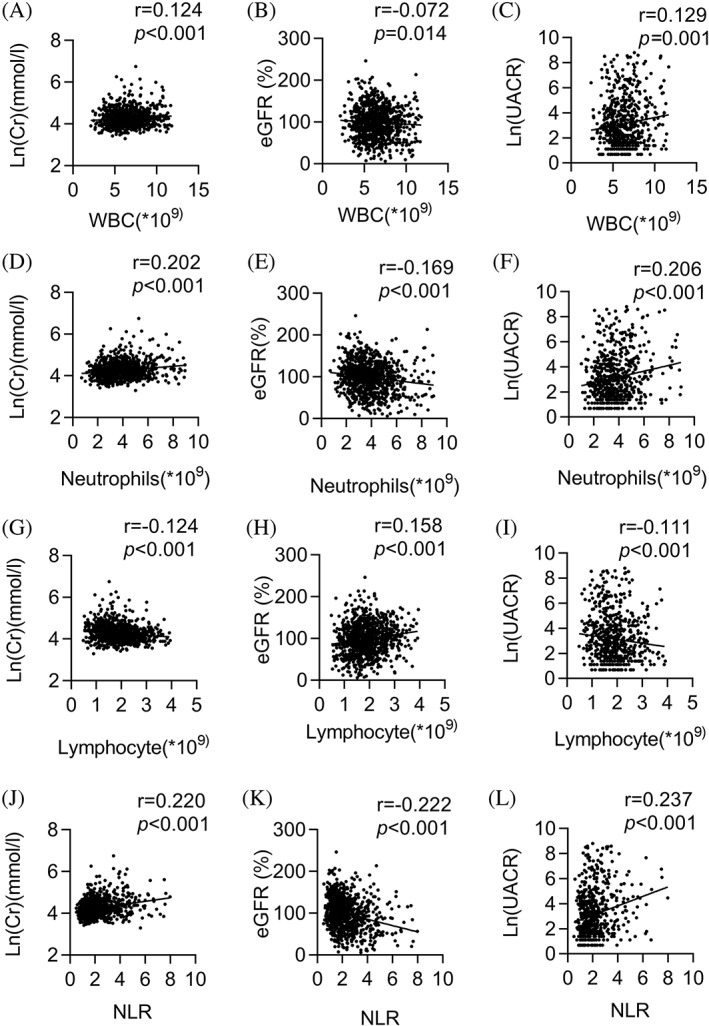
Association of WBC, neutrophil, and lymphocyte count and NLR with Cr, eGFR, and UACR. Association of WBC, neutrophil, and lymphocyte count and NLR with Cr, eGFR, and UACR. WBC count was positively associated with Cr (r = 0.124, p < 0.001) (A) and UACR (r = 0.129, p = 0.001) (C) and negatively associated with eGFR (r = −0.072, p = 0.014) (B). There was also a strong association between neutrophil count, Cr (r = 0.202, p < 0.001) (D) and UACR (r = 0.206, p < 0.001) (F) and a negative association with eGFR (r = −0.169, p < 0.001) (E). Additionally, NLR exhibited a significant and positive association with Cr (r = 0.220, p < 0.001) (J) and UACR (r = 0.237, p < 0.001) (L), but a negative association with eGFR (r = −0.222, p < 0.001) (K). Cr, creatinine; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; NLR, neutrophil‐to‐lymphocyte ratio; UA, uric acid; UACR, urinary albumin‐to‐creatinine ratio; WBC, white blood cell. e
