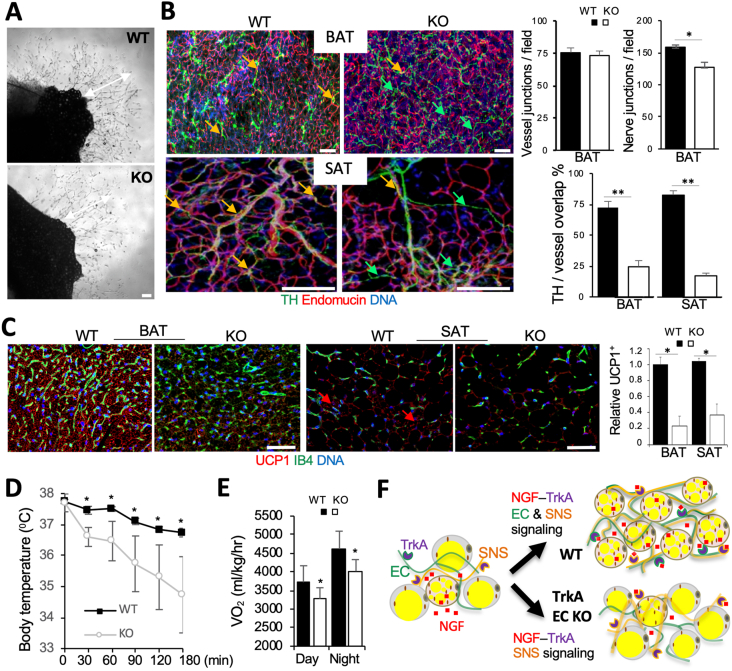
Figure 2.
Endothelial TrkA regulates AT neuro-vascular alignment and thermogenesis. (A) SAT explants at day 4 of culture show normal angiogenic sprouting (arrows) for TrkA EC KO. (B) Whole mounts subjected to IF demonstrating blood vessel (endomucin+) misalignment with nerves (TH+) in BAT and SAT of KO mice. Graphs: data quantification; Error bars: SEM ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01 (Student's t-test); N = 5 view fields. (C) Paraffin sections stained with IB4 and subjected to UCP1 IF demonstrating lower UCP1 expression in BAT and lack of beige AT (arrows) in SAT of KO mice. Graphs: relative UCP1 expression quantification; ∗P < 0.01, N = 5 view fields. Error bars: SD ∗P < 0.05 (Student's t-test). In A-C, DNA is blue; Scale bar: 50 μm. (D) Cold intolerance of male KO mice vs WT littermates, measured based on core body temperature maintenance at 4 °C. N = 6. Error bars: SD ∗P < 0.05 (Student's t-test). (E) Reduced oxygen consumption of EC KO mice during day and night. N = 5. Error bars: SEM ∗P < 0.05 (Student's t-test) calculated based on the analysis of multiple time points (Supplementary Fig. 2D). (F) A model of TrkA function in AT endothelium. NGF secreted by brown adipocytes activates TrkA in both SNS nerves and endothelial cells (EC). Endothelial TrkA signaling coordinates angiogenesis with SNS neuronal guidance, resulting in neuro-vascular network conducive of brown adipogenesis. Without endothelial TrkA, vascularization uncoordinated with SNS innervation results in reduced UCP1 expression and reduced thermogenesis.