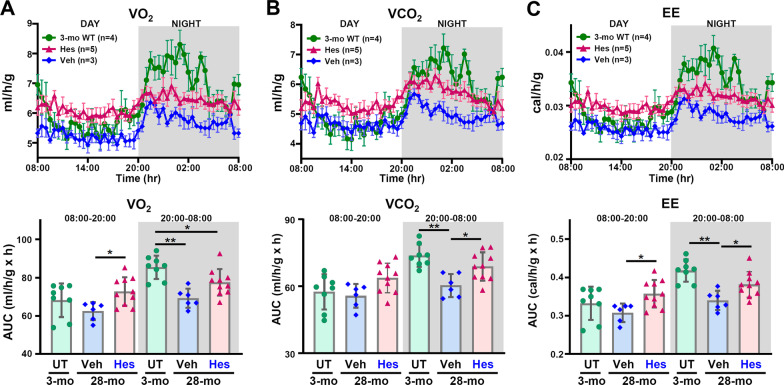
Fig. 2.
Hesperetin attenuates whole-body metabolic decline in old WT mice. Hour-to-hour average and quantification of A whole-body oxygen consumption (VO2), B CO2 production (VCO2), and C energy expenditure (EE) during the light and dark periods for 3-month WT, 28-month vehicle (Veh) treated and 28-month hesperetin (Hes) treated WT mice. The old mice (22-month old) were treated with dietary hesperetin (100 mg/kg/day) or Veh control food for 6 months and monitored at 28-month old. The metabolic rate of an individual mouse was monitored for 48 h. The area under the curve (AUC) from 20:00 to 02:00 during dark period is quantified. For each mouse, two AUC quantitative values of each metabolic index calculated from the data of two cycles of 24-h measurement are presented. Data for the VO2, VCO2, and energy expenditure are normalized to lean mass. Data are presented as mean ± SEM in the hour-to-hour metabolic monitoring. Data for quantification of AUC are presented as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.005 by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons. UT untreated