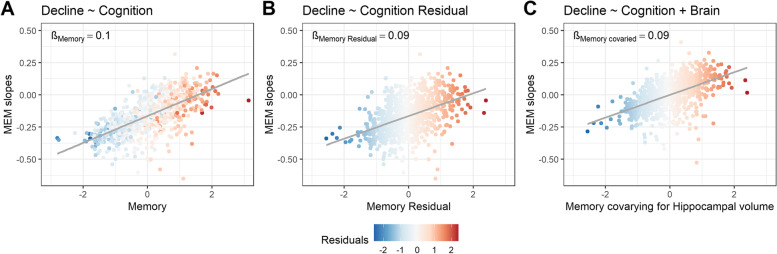
Fig. 4.
Associations with cognitive decline. Figures represent associations between annual slopes in memory (derived as the random slopes from a linear mixed effects model of memory regressed on time that included the whole sample) and A memory at baseline, B residuals of baseline memory regressed on hippocampal volume, and C baseline memory when hippocampal is also included as a predictor in the model. This figure illustrates that the regression coefficient (β) estimated for the memory residual in panel B (a linear regression of the form “Slopes ~ Residual”) is equivalent to the coefficient of the cognition term in a multivariable regression that includes both cognition and brain as predictors of decline (slopes ~ memory + hippocampal volume) shown in panel C. Note that panel C is a partial regression plot, in which the data points illustrate the relationship between memory slopes and cognition when covarying for brain. MEM = ADNI memory factor score