Fig. 5: Effect of BPA, BPS, EE2 and their combinations on serum, testicular and Leydig cell testosterone (T) concentrations in prepubertal male rats.
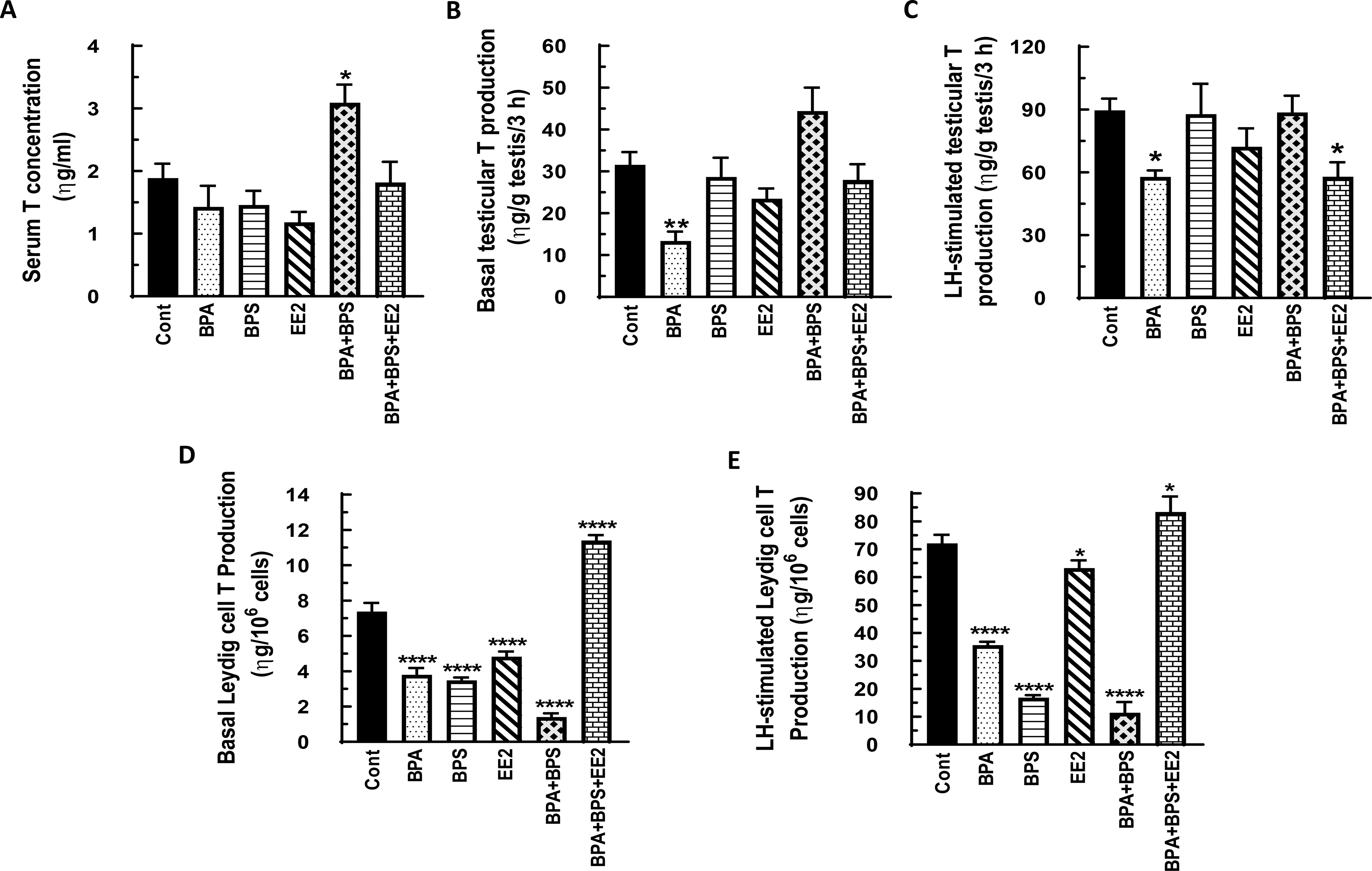
Long-Evans male rats at 21 days of age (n=48) were fed drinking water containing BPA, BPS, or EE2 (5 μg/L) or their combinations BPA+BPS (2.5 μg/L) each and BPA+BPS+EE2 (1.7 μg/L) each for 14 days. At sacrifice, blood was processed to obtain serum (A). Testicular explants were obtained and incubated in DMEM/Ham’s F-12 culture medium in triplicate without (basal, B) or with 100 ηg/ml ovine LH (NIDDK, NIH) (LH-stimulated, C) for 3 h. In addition Leydig cells were isolated and incubated in DMEM/Ham’s F-12 culture medium without (basal, D) or with 100 ng/ml ovine LH (NIDDK, NIH) (LH-stimulated, E) for 3 h. Aliquots of serum and spent media were analyzed to measure T concentrations by RIA (n = 8; *p < 0.05, **p <0.001, ***p < 0.0001).
