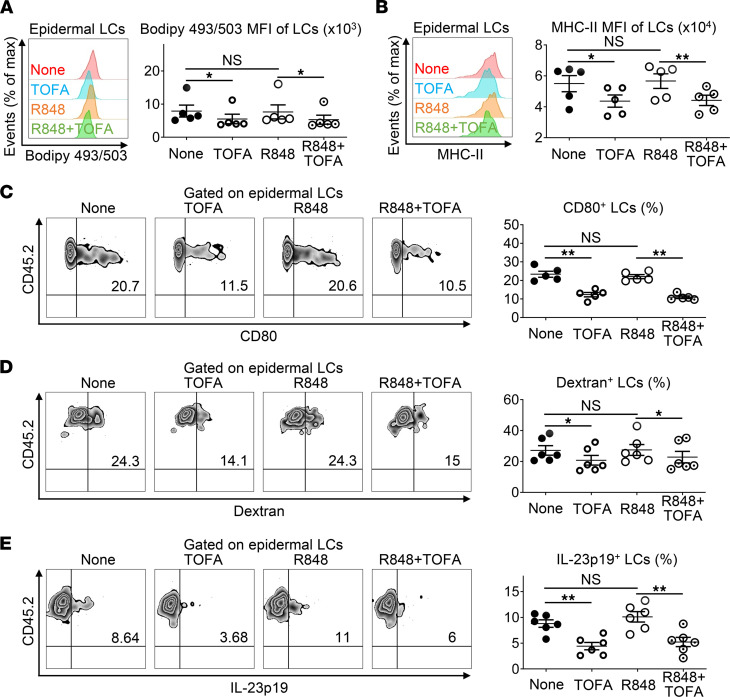
Figure 4. Inhibition of fatty acid synthesis alters the immunofunctions of epidermal LCs.
(A–E) Epidermal cells freshly isolated from WT C57BL/6J mice were in vitro cultured with or without Resiquimod (R848, 2 μg/mL) or/and TOFA (10 μg/mL) for 18 hours (A–C) or 24 hours (D and E) with or without Golgi Stop for the last 4 hours. (A–C) Cells were stained with anti–MHC-II, anti–CD45.2, anti–CD80 Ab and Bodipy 493/503, which were analyzed by flow cytometry (n = 20, 3 independent experiments). Histogram and MFI of Bodipy 493/503 (A) and MHC-II (B) in epidermal LCs. (C) Representative FACS analysis and the ratios of CD80+ LCs. (D) Cells were incubated with dextran-FITC at 37°C for 45 minutes and stained with anti–MHC-II and anti–CD45.2. Representative FACS analysis and the ratios of dextran+ LCs (n = 24, 3 independent experiments). (E) Cells were stained with anti-MHC-II, anti–CD45.2 and anti–IL-23p19. Representative FACS analysis and the ratios of IL-23p19+ LCs (n = 24, 3 independent experiments). Two-tailed Student’s t test was performed. Tests were considered significant with P < 0.05 after multiple testing adjustments by the FDR method. The data are presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.