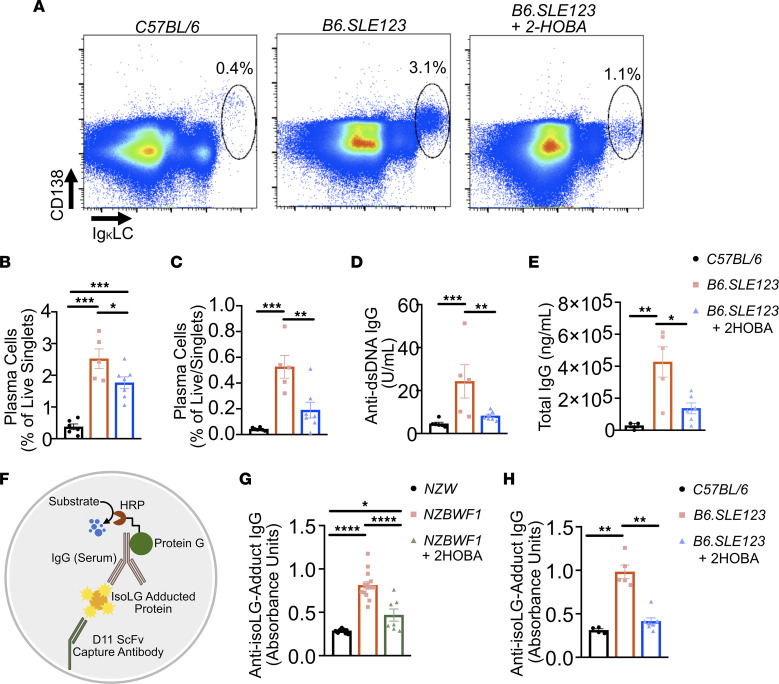
Figure 7. Plasma cell accumulation, autoantibody production, and anti-isoLG IgG levels are attenuated by 2-HOBA in a mouse model of SLE.
Cells were isolated from 32-week-old B6.SLE123 mice. Single-cell suspensions were prepared from freshly isolated mouse tissue via enzymatic digestion and mechanical dissociation. Live cell singlets were analyzed. (A) Representative FACS plots displaying CD138+ and intracellular Ig κ light chain+ plasma cells from bone marrow. Quantitation of plasma cells as a percentage of live singlet cells for (B) spleen and (C) bone marrow. (D) Anti-dsDNA IgG antibody and (E) total IgG at 1:100,000 dilution were quantified from plasma using ELISA. Data were analyzed by 1-way ANOVA (n = 5–8, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001). Serum was collected from mice at the time of sacrifice at 32 weeks old. Antibodies against isoLG adducts were determined by ELISA from serum. (F) Model of capture assay to detect anti-isoLG adduct IgG. The D11 ScFv single-chain antibody was bound to a plate. Kidney protein was adducted with isoLG in vitro and incubated with D11 ScFv. Serum from lupus-prone mice was then added, and after extensive washing, the presence of bound IgG was detected utilizing a protein-G HRP conjugate. Anti-isoLG adduct IgG was detected in (G) NZBWF1 mice treated with vehicle or 2-HOBA compared with NZW controls and (H) B6.SLE123 mice treated with vehicle or 2-HOBA compared with C57BL/6 controls. Data were analyzed with 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test (n = 4–7 for B6.SLE123, n = 7–14 for NZBWF1; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001).