Figure 7.
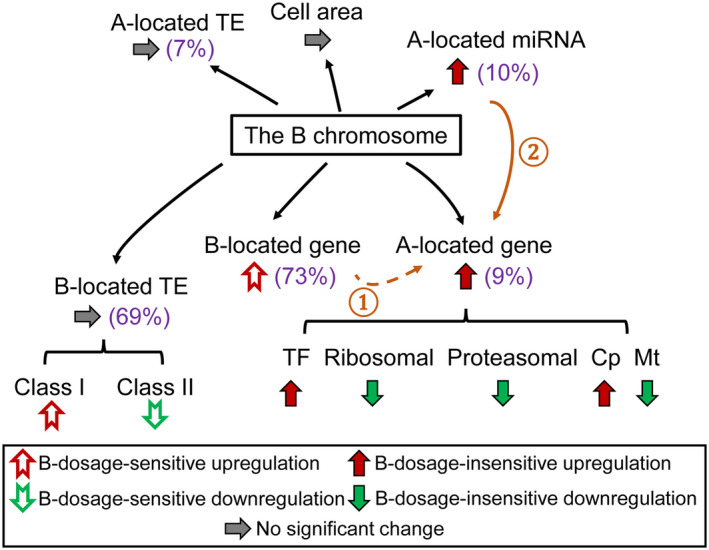
Summary of the impact of the B chromosome. Values in brackets represent the percentage of B‐dosage‐sensitive genes, miRNAs, and TEs, respectively. Varied B dosage leads to an overall B‐dosage‐insensitive upregulation of A‐located genes and miRNAs, with genes from different functional classes responding differently. Ascending B copy number causes a trend of B‐dosage‐sensitive upregulation of B‐located genes. Although no global change is observed for A‐ and B‐located TEs, B‐located TEs from different classes show trends of B‐dosage‐sensitive effects. Cell area does not vary significantly with an increase of B dosage. ①: B‐dosage‐sensitive A‐located genes are likely to be regulated by B‐dosage‐sensitive B‐located genes. ②: A‐located miRNAs modulate the expression of A‐located targets in a B‐dosage‐insensitive manner.
