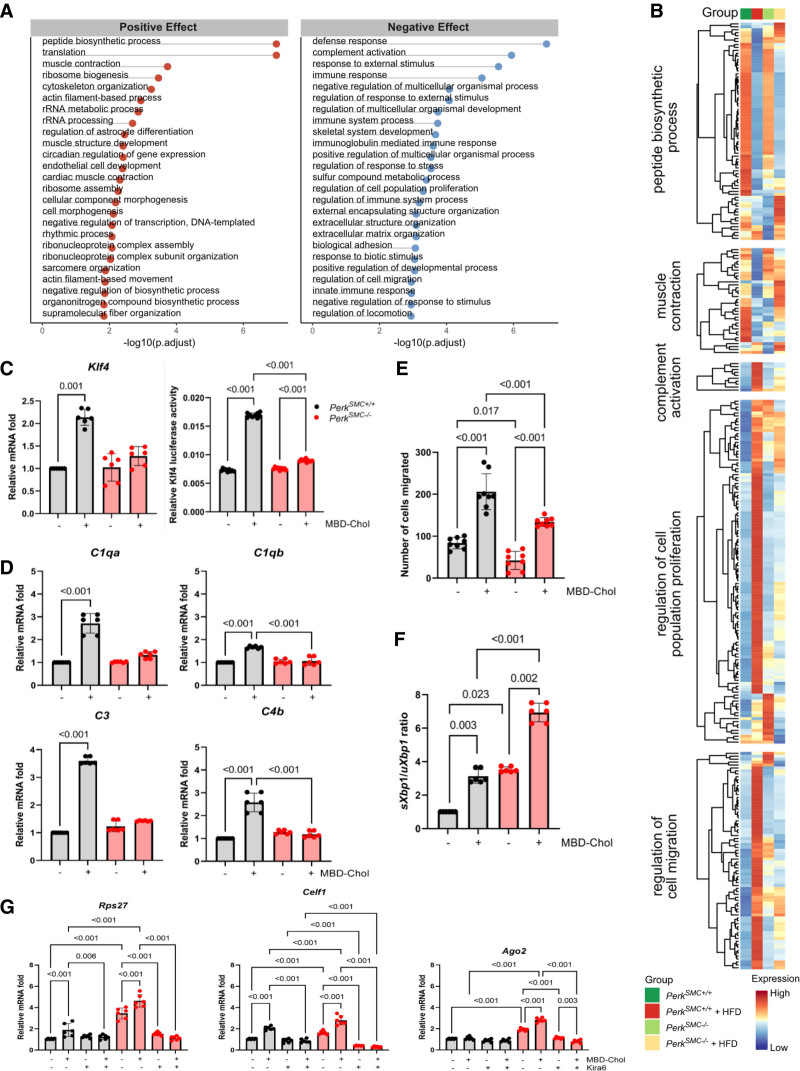
Figure 3.
Contractile smooth muscle cell (SMC) clusters in the hypercholesterolemic PerkSMC+/+ mice activate Perk signaling. A, Gene ontology (GO) enrichment analysis of the DEGs identified the Top 25 up- and downregulated pathways altered specifically with loss of Perk signaling in contractile SMCs. B, Heatmap of the genes up- and downregulated in select pathways in contractile SMCs that are specifically altered due to deletion of Perk. C, Cholesterol-induced increases in expression and transcriptional activation of Klf4 are abrogated by Perk deletion in explanted PerkSMC−/− SMCs. D, Cholesterol-induced increased expression of the complement pathway components C1qa, C1qb, C3, and C4b in SMCs is abolished by the deletion of Perk. E, Perk deletion reduces migration of SMCs. F, The Ire1 arm of unfolded protein response is upregulated in PerkSMC−/− SMCs and is further activated by cholesterol treatment. G, Ribonuclear protein assembly associated genes are upregulated at baseline in PerkSMC−/− SMCs and show further activation with cholesterol exposure, and this increased expression is abrogated by the chemical inhibition of Ire by Kira6. All qPCR data were analyzed by Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn multiple comparisons test. Data are represented as mean±SD. HFD indicates hypercholesterolemia followed by high-fat diet.