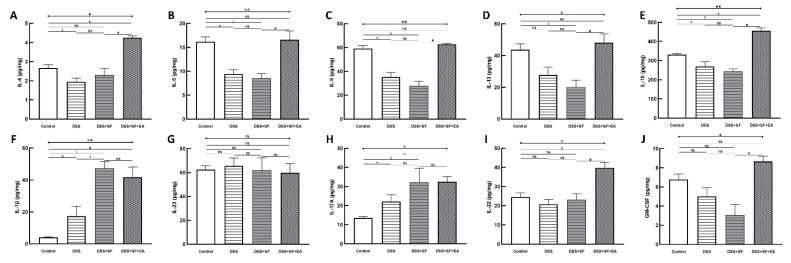
Figure 4.
Electroacupuncture effect in colonic immunoassay in dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis in sleep fragmented C57BL/6 mice. (A) IL-4, (B) IL-5, (C) IL-9, (D) IL-13, (E) IL-10, (F) IL-1β, (G) IL-23, (H) IL-17A, (I) IL-22, and (J) GS-CSF concentration in colon tissue in four groups. Electroacupuncture performed significant increasement in Th2/ILC2 related cytokines (A–E), as well as ILC3-derived IL-22 and GM-CSF (I,J), but showed no obvious change over IL-1β, IL-23, and IL-17A (F–H). * Stands for a result of four groups comparison (represented by bold line segments with endpoints). ✠, ✟, #, $ and & represent the results of control group versus DSS group, DSS group versus DSS + SF group, DSS + SF group versus DSS + SF + EA group, control group versus DSS + SF group, and control group versus DSS + SF + EA group, respectively (represented as a thin line without endpoints). *, ✠, ✟, #, $, &, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ns, no significance. Data were presented as mean ± SEM of four mice in each group. DSS, dextran sodium sulfate; SF, sleep fragmentation; EA, electroacupuncture; IL, interleukin; GM-CSF, Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; ILC, innate lymphoid cells.