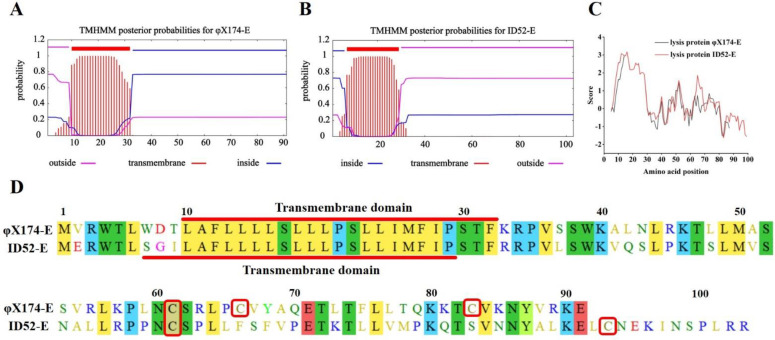
Figure 6.
Transmembrane domain prediction, hydrophilicity analysis and amino acids sequence alignment of lysis proteins E. (A,B): Transmembrane domain prediction of proteins φX174−E and ID52−E performed by TMHMM Server 2.0, respectively; (C): The hydrophilicity analysis of proteins φX174−E and ID52−E performed by ExPASy online tool Protscale; (D): The amino acids sequence alignment of lysis protein performed by Molecular Evolutionary Genetics. The NCBI Reference Sequence of lysis protein φX174−E: NP_040709.1; The NCBI Reference Sequence of lysis protein ID52−E: YP_512455.1. The color represented the similarity of amino acids, and the same color meant that the amino acid residues of the two lysis proteins were the same or the characteristics were very similar. The red box represented the cysteine contained in the lysis proteins.