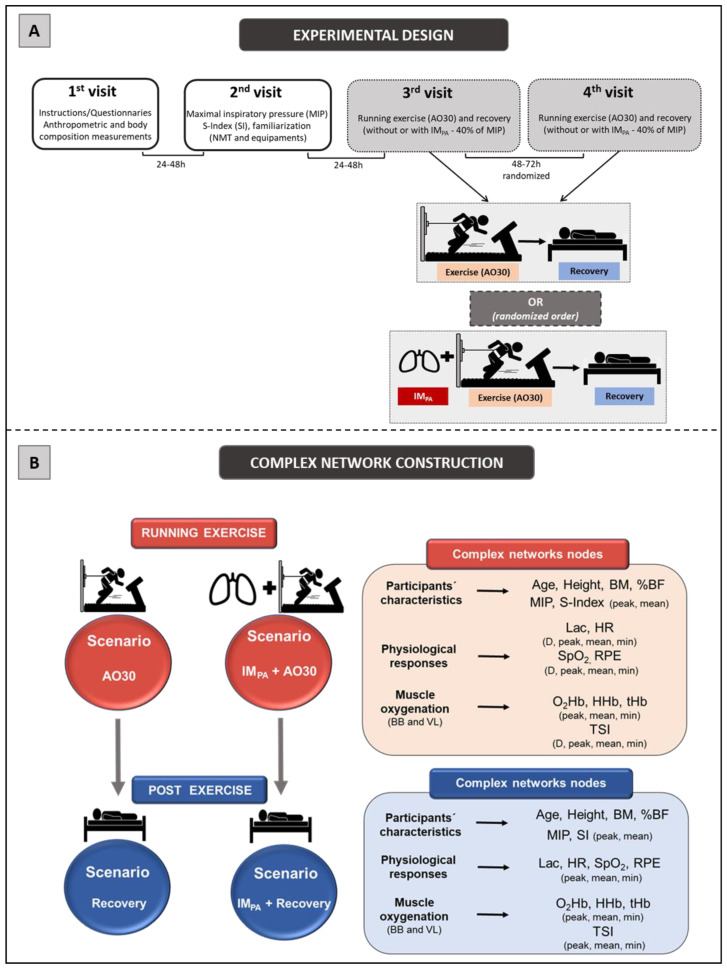
Figure 1.
Panel A.Experimental design. First and second visits were conducted for sample characterization and familiarization. Additionally, the maximal inspiratory pressure (MIP) and global strength index of inspiratory muscles (SI) were measured. Exercise (all-out in tethered running, AO30) and recovery (both, without or with inspiratory muscle pre-activation (IMPA)) were conducted at the third and fourth randomized visits, separated by 48–72 h. Panel B. Scenarios for constructing the complex networks and complex network nodes used in these four scenarios. Legend: AO30 = all-out 30 s, IMPA = inspiratory muscle pre-activation, BM = body mass, %BF = percentage of body fat, MIP = maximal inspiratory pressure, SI = global strength index of inspiratory muscles, Lac = blood lactate, HR = heart rate, SpO2 = arterial oxygen saturation, RPE = perceived exertion, D = delta between final and initial results, BB = biceps brachii, VL = vastus lateralis, O2Hb = oxyhemoglobin relative concentration, HHb = deoxyhemoglobin relative concentration, tHb = total hemoglobin, TSI = tissue saturation index.