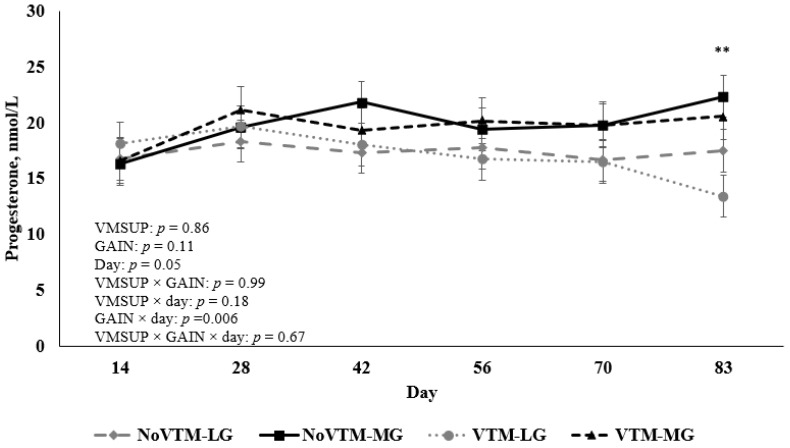
Figure 4.
Effect of vitamin and mineral supplementation [VMSUP; supplemented (VTM) vs. unsupplemented (NoVTM); from pre-breeding to d 83 of gestation] and two different rates of gain [GAIN; low gain (LG), 0.28 kg/d, vs. moderate gain (MG), 0.79 kg/d; from breeding to d 83 of gestation] on progesterone (P4) concentrations. NoVTM-LG (n = 9): No vitamin and mineral supplement, low gain; NoVTM-MG (n = 9): No vitamin and mineral supplement, moderate gain; VTM-LG (n = 9): Vitamin and mineral supplement, low gain; VTM-MG (n = 8): Vitamin and mineral supplement, moderate gain. A rate of gain × Day interaction (p = 0.006) was observed for P4 concentrations, which were similar between LG (low gain, 0.28 kg/d) and MG (moderate gain, 0.79 kg/d) on d 14 to 70; and were greater (p = 0.05) for MG compared with LG on d 83, as indicated by **. Values are least squares means, with error bars depicting standard error.