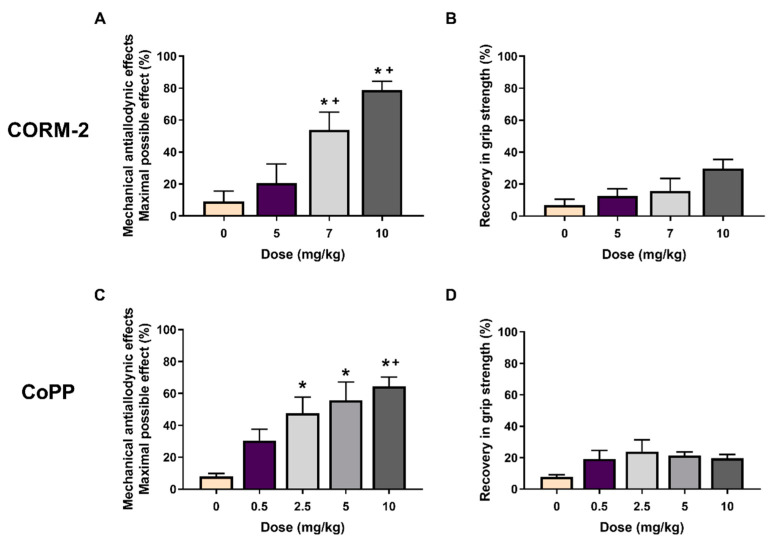
Figure 2.
CORM-2 or CoPP treatments inhibited the mechanical allodynia but not the grip strength deficit induced by MIA in a dose-dependent manner. Mechanical antiallodynic (A,C) and the recovery in grip strength (B,D) effects induced by different doses of CORM-2 or CoPP (mg/kg) are represented. For each test and treatment, * indicates significant differences vs. vehicle (0 mg/kg)-treated mice and + vs. the effect produced by low doses of CORM-2 (5 mg/kg) or CoPP (0.5 mg/kg) (p < 0.05; one-way ANOVA, followed by the Student–Newman–Keuls test). Data are expressed as the mean values of the maximal possible effect (%) for the mechanical allodynia and the recovery in grip strength (%) ± SEM; n = 6 animals per dose and treatment.