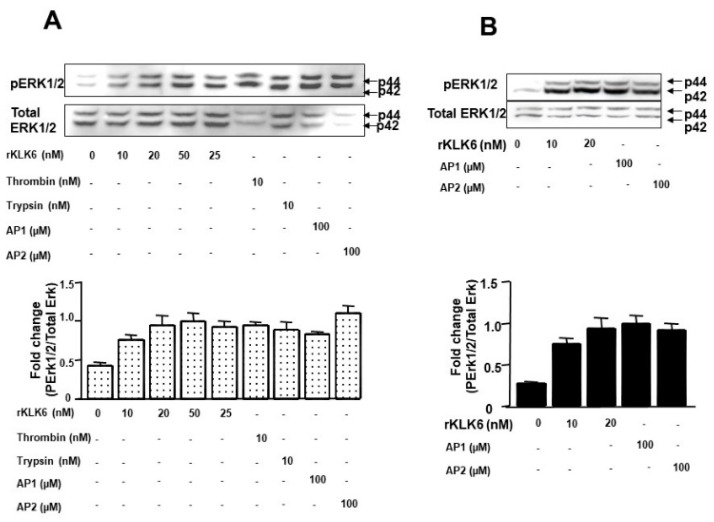
Figure 4.
Dose-dependent activation of p42/p44 MAP-Kinase phosphorylation by KLK6. (A) Quiescent HT-29 cells were stimulated with the indicated concentrations of KLK6, thrombin (0.01 µmol/L), trypsin (0.01 µmol/L), with 100 µM of TFLLR-NH2 (AP1, a PAR1 agonist), 100 µM SLIGKV-NH2 (AP2, a PAR2 agonist) or with vehicle (control) for 5 min. (B) Quiescent HCT116 cells were stimulated with the indicated concentrations of KLK6, with 100 µM of TFLLR-NH2 (AP1, a PAR1 agonist), with 100 µM SLIGKV-NH2 (AP2, a PAR2 agonist) or with vehicle (control) for 5 min. To confirm equal protein loading, the membranes were stripped and incubated with p42/p44 MAP-Kinase antibody. p42/p44 MAPKinase protein seems to be reduced in PARs agonist-stimulated samples, possibly because the high signal with the anti-phopsho-ERK1/2 (Thr202/Tyr204) antibody prevents subsequent anti-ERK1/2 antibody binding to the ERK1/2 epitope as observed previously [9]. Densitometric analysis of the phospo-p42/p44 MAP-Kinase divided by total amount of p42/p44 MAP-Kinase is represented in lower panels. Results are representative of two separate experiments.