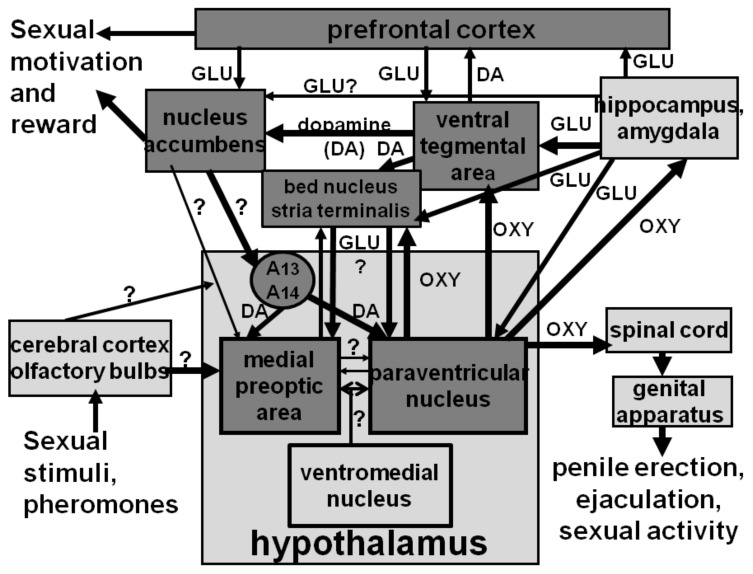
Figure 3.
Dopamine participates in a complex central neural circuit that controls and influences sexual motivation and reward and copulatory performance at the central level together with other neurotransmitters and/or neuropeptides. This neural circuit interconnects the hypothalamus and its nuclei (paraventricular and ventromedial nuclei) with areas of the limbic system (ventral tegmental area, hippocampus, amygdala, bed nucleus of the stria terminalis), with the ventral medulla and the spinal cord. Among involved dopaminergic pathways are (i) incertohypothalamic dopaminergic neurons, which activate PVN oxytocinergic neurons that send their projections to the ventral medulla and spinal cord and to the ventral tegmental area, hippocampus, amygdala and bed nucleus of the stria terminalis; (ii) mesolimbic/and mesocortical dopaminergic neurons that originate in the ventral tegmental area that send projections to the nucleus accumbens, medial prefrontal cortex, bed nucleus of the stria terminalis and possibly to the hippocampus and amygdala. Together with glutamatergic neurons that interconnect the hippocampus and the amygdala with the ventral tegmental area, prefrontal cortex, bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, medial preoptic area and paraventricular nucleus, when this circuit is activated for instance by physiological stimuli (i.e., pheromones released by a sexually receptive female) or by drugs or peptides administered in one of the areas of the circuit (i.e., oxytocin injected into the ventral tegmental area, the hippocampal ventral subiculum or the amygdala), dopamine becomes active at different sites, i.e., in the paraventricular nucleus and the medial preoptic area, which are involved more in copulatory performance (penile erection and copulation), and in the nucleus accumbens in which dopamine plays a main role in sexual motivation, arousal and reward (heavy gray boxes indicate the brain areas of the circuit in which dopamine is involved/released). Thus, modifications in dopamine activity in these brain areas participate in the regulation of sexual motivation/arousal/reward and copulatory performance (erectile function/copulation) (for references see [82,100,102]).