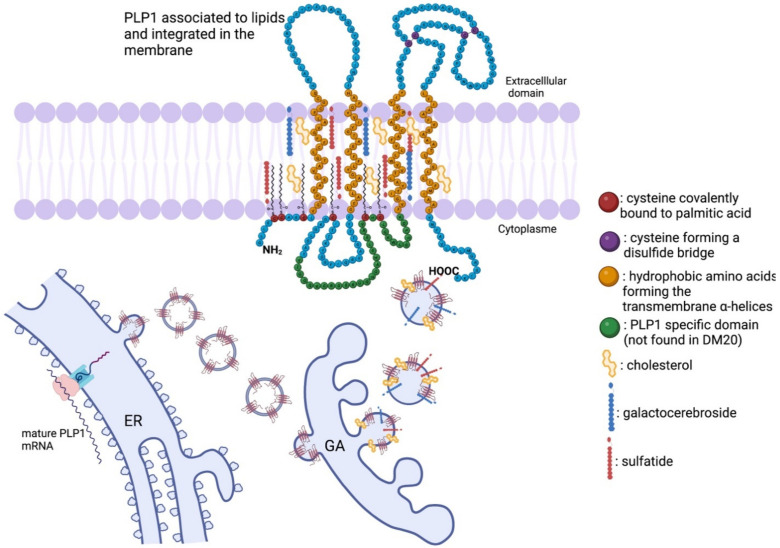
Figure 3.
The physiological state of PLP1 formation: from mRNA to a functional transmembrane protein. The mature mRNA encoding PLP1 is translated in the rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Afterward, the immature protein is transported to the Golgi apparatus (GA), where it will associate with lipidic myelin components, such as cholesterol, galactocerebrosides, and sulfatides to form lipidic rafts. Then, the lipidic rafts are sent toward the cellular membrane to form the myelin sheath. PLP1 is a 30 kDa tetraspan transmembrane protein with NH2 and COOH termini in the cytoplasm. It has four transmembrane α-helices inside the membrane of oligodendrocytes, and it is a highly hydrophobic protein. Palmitic acid is covalently bound to PLP1 via six cysteine residues by an autocatalytic posttranslational modification. The fatty acids attached to the intracellular loop of PLP1 ensure the integration of this protein in the lipid leaflet in compact myelin.