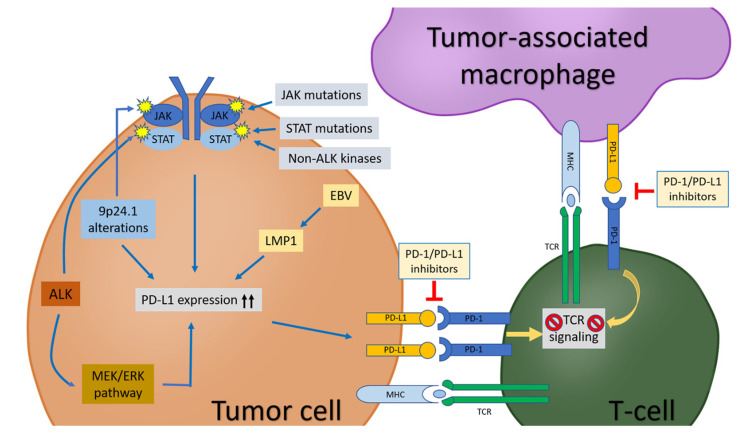
Figure 1.
The PD-1/PD-L1 pathway in tumor cells, tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), and T-cells in tumor microenvironment. PD-L1 expression in tumor cells is upregulated by: (1) chromosome locus 9p24.1 alterations (polysomy, copy gain, amplification, translocation, etc.); (2) activation of JAK/STAT pathway due to chromosome locus 9p24.1 alterations, kinases (such as ALK and non-ALK), JAK/STAT mutations; (3) EBV infection; (4) MEK/ERK pathway. PD-L1 on tumor cells and/or TAMs interact with PD-1 on T-cells, leading to inhibition of T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling pathway and subsequent T-cell “exhaustion”. Blockade of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway can release T-cells from the inhibitory effects by tumor cells and/or TAMs and re-establish the T-cell-mediated antitumor immune response.