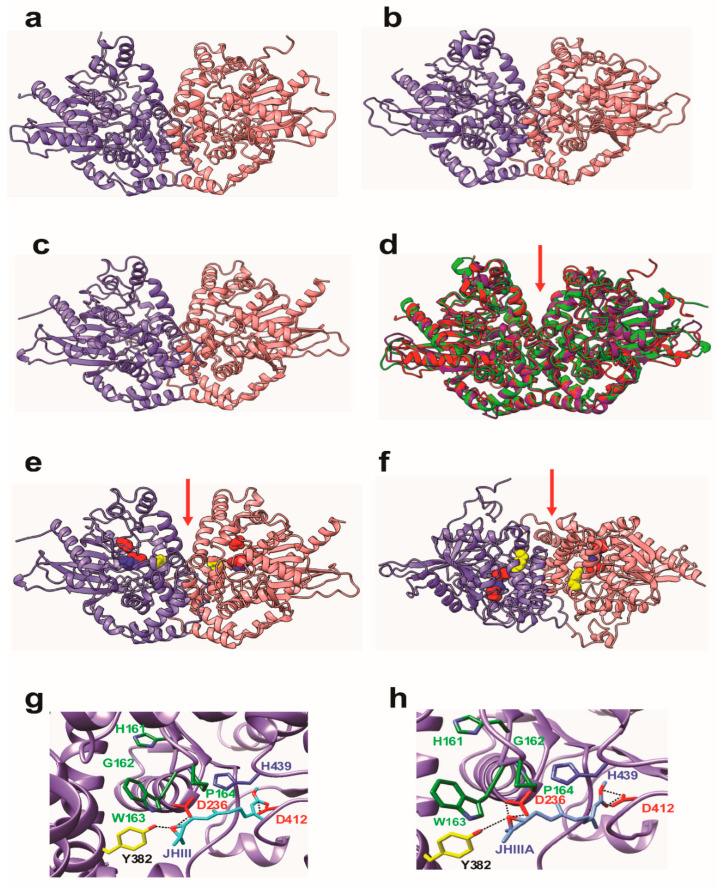
Figure 4.
3D models showing non-covalently associated homodimeric monomers of (a) JHEH 1 (b) JHEH 2 and (c) JHEH 3. The two monomers are colored violet and pink, respectively. (d) Superpositioning of the 3 models built for JHEH 1 (red), JHEH 2 (blue) and JHEH 3 (green) showing good superposition of the α-helices and β-sheets forming the backbones of the homodimers. The red arrow indicates the depression separating both monomers, associated with the catalytic grooves of both monomers. (e) Lateral view and (f) upper view of JHEH 3 homodimer showing the localization of residues D236 (red), Y382 (yellow), D412 (red) and H439 (blue) forming the catalytic grooves located on either side of the central depression (red arrow). (g). Docking of juvenile hormone III (JH III) (colored cyan) to the catalytic groove of JHEH 3. Amino acid residues D236, D412 and H439 forming the catalytic triad of JHEH 3 are colored red and blue, respectively. Tyrosine residue Y382, forming a H-bond with the epoxide group of JH III, is colored yellow. Amino acid residues from the HGWP motif are colored dark green. Hydrogen bonds are indicated by black dashed lines. (h). Docking of juvenile hormone III acid (JH IIIA) (colored blue), to the catalytic groove of JHEH 3. Amino acid residues D236, D412 and H439 forming the catalytic triad of JHEH 3 are colored red and blue, respectively. Tyrosine residue Y382, forming a H-bond with the epoxide group of JH IIIA, is colored yellow. Amino acid residues from the HGWP motif are colored dark green. Hydrogen bonds are indicated by black dashed lines. Note that only 2 H-bonds out of total 4 H-bonds of D412 with JH IIIA can be seen at this viewing angle.