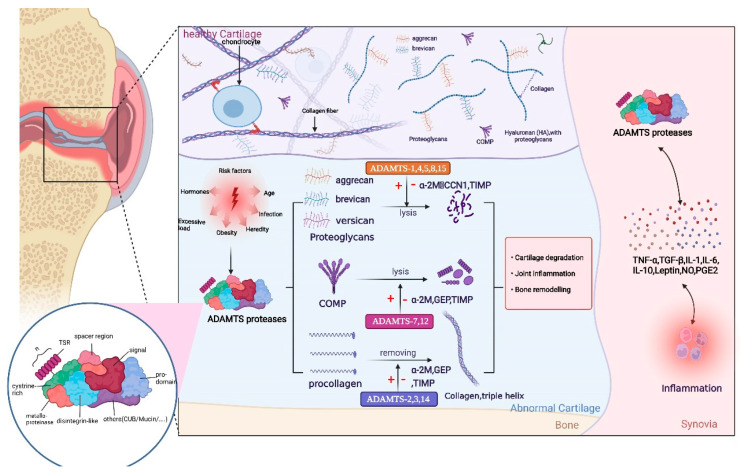
Figure 1.
Structure of the ADAMTS proteases includes a signal peptide, variable-length anterior domain, metalloproteinase domain, integrin-like domain, central thrombospondin type 1 sequence repeat (TSR) motif, cysteine-rich spacer domain, and auxiliary domain. The auxiliary domain determines the differences among members of the ADAMTS protein family. The role of ADAMTS proteases is mainly reflected in the following aspects: first, ADAMTS proteases degrade various proteoglycans, especially aggrecan. Second, ADAMTS proteases cleave the amino-terminal of procollagen and promote the spontaneous assembly of procollagen into collagen fibers. Moreover, ADAMTS proteases also degrade COMP, an important non-collagen protein in the cartilage. ADAMTS regulates the release and expression levels of inflammatory factors by activating or inhibiting relevant signaling pathways; thus, completing a series of physiological function. Owing to some risk factors, including hormones, age, obesity, mechanical load, injury, and infection, these processes tend to be abnormal and decomposition is accelerated; thus, contributing to the development of osteoarthritis (OA). This figure has been created with https://app.biorender.com (accessed on 24 May 2022).