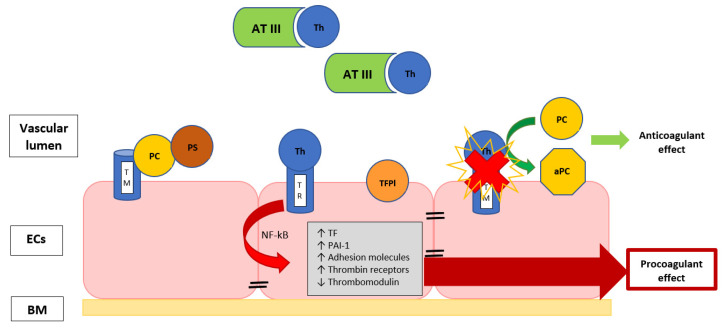
Figure 1.
The image describes the EC surface with thrombomodulin, a thrombin-binding protein that is responsible for thrombin activity inhibition. When thrombin is bound to TM, they form an activator complex for PC, conferring the anticoagulant properties. The exposure to inflammatory and/or septic stimuli rapidly causes the internalization of TM or the release of inactivated TM, favoring the thrombin binding with its receptor, leading to the endothelial modulation ability towards a procoagulant state. Th, thrombin; TR, thrombin receptor; TM, thrombomodulin; AT III, antithrombin III; TFPI, tissue factor pathway inhibitor; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; PAI-1, plasminogen activator inhibitor; TF, tissue factor; BM, basal membrane; ECs, endothelial cells; PC, protein C; aPC, activated protein C; PS, protein S.