Figure 7.
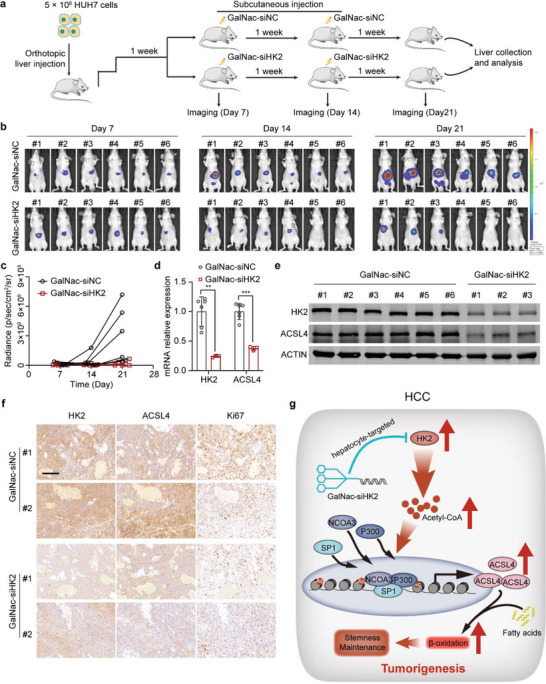
GalNac‐siHK2 administration effectively attenuates the growth of orthotopic tumor xenografts in vivo. a) A schematic diagram of the orthotopic tumor xenograft studies. HUH7 cells stably expressing GFP‐luciferase were injected into the livers of BALB/c nude mice in situ. After 7 d, mice were separated into two groups (n = 6) and treated with negative control (GalNac‐siNC) or GalNac‐siHK2 (5 mg kg−1). GalNac‐siHK2 was treated every 7 d. In vivo imaging to analyze the tumor growth. b) In vivo images showing the tumor growth of mice treated with the negative control and GalNac‐siHK2. c) Statistics of the radiance abundance of in vivo images. d) Real‐time qPCR showing HK2 and ACSL4 mRNA expression in tumor samples of the negative control and GalNac‐siHK2 treatment groups. Data are represented as the mean ± SD (n = 6 or 3, respectively). Unpaired t‐test. e) Western blots measuring HK2 and ACSL4 expression in tumor samples of the negative control and GalNac‐siHK2 treatment groups (n = 6 or 3, respectively). f) Immunohistochemistry was used to analyze the expression of HK2, ACSL4, and Ki67 in orthotopic tumor xenograft samples. Scale bar represents 100 µm. g) The working model shows that HK2 stimulates maintenance of stemness and self‐renewal of liver CSCs. Upregulated HK2 expression promoted the levels of acetyl‐CoA in HCC cells. HK2 accumulates acetyl‐CoA in HCC cells, induces promoter and enhancer histone acetylation, and activates the transcription of ACSL4, thus providing fatty acids for β‐oxidation. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
