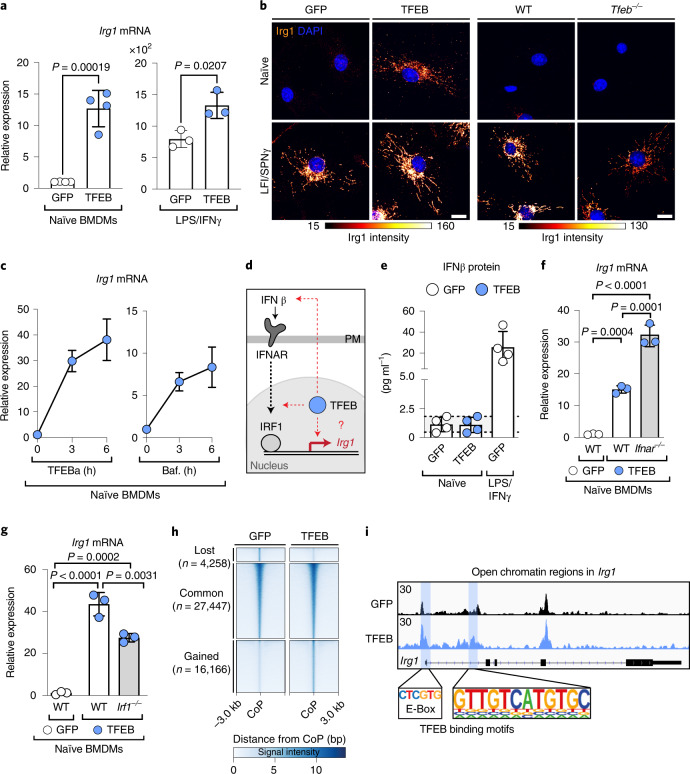
Fig. 3. TFEB activation induces transcription of Irg1.
a, Relative Irg1 mRNA expression determined by real-time qPCR in naïve or 6 h LPS/IFNγ-treated TFEB-GFP- or GFP-expressing BMDMs. Bars show mean ± s.d. of n = 4 (left) n = 3 (right) independent experiments. P values were calculated using unpaired, two-sided Student’s t-test. b, Images of endogenous Irg1 visualized by immunofluorescence and treated without or with LPS/IFNγ for 6 h in (left) WT BMDMs expressing GFP- or TFEB-GFP, or (right) Tfeb−/− and control BMDMs. Images are representative of n = 3 independent biological experiments. Scale bar, 10 µm. c, Irg1 mRNA expression in BMDMs treated with 5 mM TFEBa or 100 nM Baf. Line graphs show the mean ± s.e.m. of n = 3 (TFEBa) and n = 5 (Baf) independent experiments. d, Schematic of potential mechanisms of TFEB-driven Irg1 expression. e, Quantification of secreted IFNβ protein from naïve TFEB-GFP and GFP-expressing BMDMs. LPS/IFNγ-treated, GFP-expressing BMDMs served as positive control. Bars show mean ± s.d. of n = 4 independent experiments. f,g, Relative Irg1 mRNA expression in naïve WT, Ifnar1−/− (f) or Irf1−/− (g) BMDMs, expressing TFEB-GFP or GFP. Bars show mean ± s.d. of n = 3 independent experiments. P values were calculated using one-way ANOVA, with Tukey’s post hoc. h, Heatmap depicting differentially accessible regions in GFP- and TFEB-GFP-expressing BMDMs, using a window of ±3 kb from the centre of the peak (CoP). Three clusters are represented denoting the commonly (common) accessible sites and the regions that loose or gain accessibility upon TFEB expression (lost and gained, respectively). i, Representative gene tracks from ATAC-seq data of the Irg1 gene region. Blue boxes indicate significantly gained peaks in TFEB-GFP- relative to GFP-expressing BMDMs. The y axis represents the reads per kilobase of transcript per million of mapped reads. Potential TFEB binding sites, derived from motif analysis are highlighted. Data show n = 1 experiment with n = 2 technical repeats.