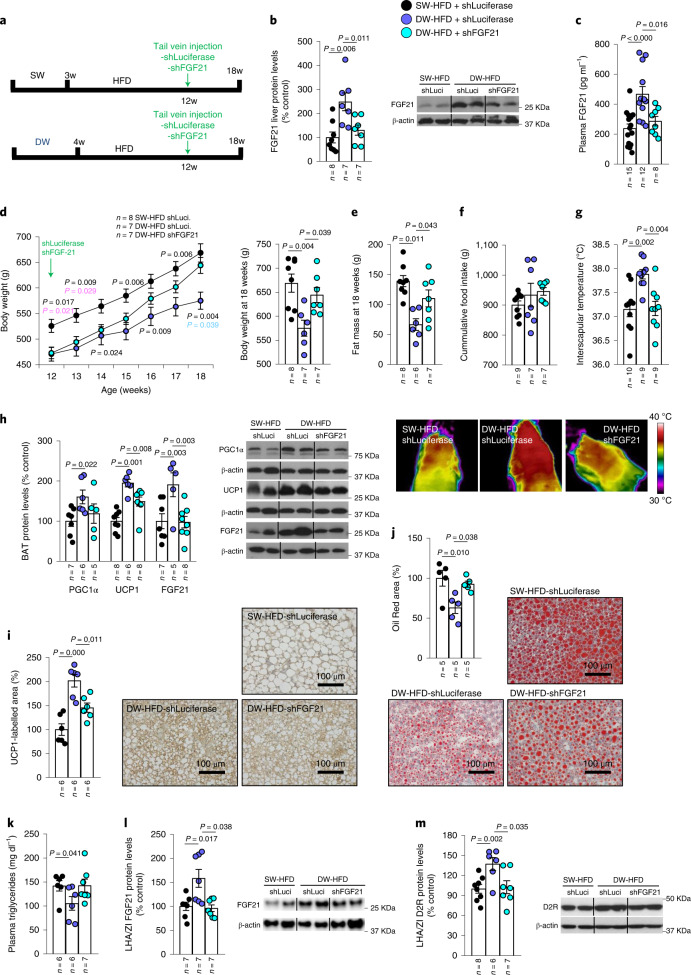
Fig. 4. Knockdown of Fgf21 in the liver blunts delayed-weaning-induced weight loss.
a, Timeline of the experimental protocol. b–m, Effect of infection with adenoviral particles encoding shFgf21 in the tail vein of 12-week-old rats fed an HFD after prolonged suckling on liver protein levels of FGF21 (b); plasma FGF21 levels (c); body weight (d); fat mass (e); cumulative food intake (f); infrared thermal images and quantification of BAT interscapular temperature (g); BAT protein levels of PGC1α, UCP1 and FGF21 (h); quantification of immunolabelling for UCP1 in BAT (i); Oil Red area in the liver (j); plasma triglycerides (k); LHA/ZI protein levels of FGF21 (l); and LHA/ZI protein levels of D2R (m). Protein data were expressed as percentages in relation to control (SW-HFD shLuciferase) animals. β-actin was used to normalize protein levels. Dividing lines indicate splicing within the same gel. Values are represented as means ± s.e.m., n per group. Exact P values are shown. Statistical differences were determined by one-way ANOVA (normal data and homogeneity of variances) followed by Tukey’s post hoc multiple-comparison test (c–e, g and i–k) or a two-sided Mann–Whitney U test (non-normal data and non-homogeneous variance; b, f, h, l and m).