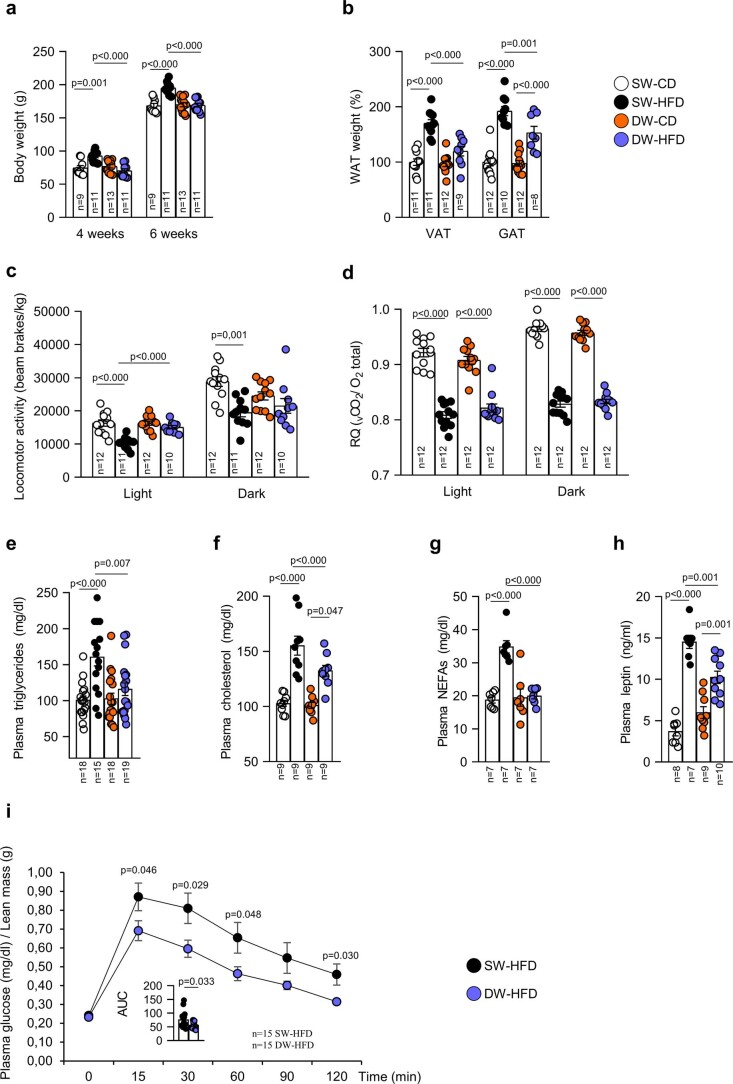
Extended Data Fig. 1. Prolonged breastfeeding decreases fat mass and improves dyslipidemia.
a–h, Delayed weaning effects on body weight (a), white adipose tissue (WAT) weight in terms of the weight of Visceral Adipose Tissue (VAT) and Gonadal Adipose Tissue (GAT) (n = 8–12) (b); locomotor activity (c); respiratory quotient (RQ) (d); circulating levels of triglycerides (e), cholesterol (f), non-esterified fatty acids (NEFAs) (g), and leptin (h). i, Delayed weaning effects on glucose tolerance normalized with lean mass. Values are represented as means ± SEM, n per group indicated in each figure. Exact P values are shown. Statistical differences according to a One-way analysis of variance ANOVA (normal data and homogeneity of variances) followed by Tukey’s post hoc multiple comparison test (a, b, c, d, g and h) or to a two-sided Student’s t-test (normal data) (i), a two-sided Mann-Whitney U-test (non-normal data and non-homogeneous variance) (e and f).