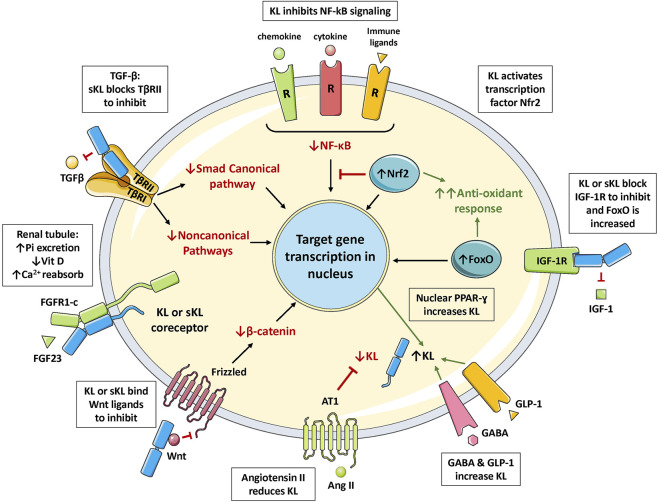
FIGURE 3.
The multiple functions of Klotho. FGF23 binds to Klotho/FGFR1c receptor in the renal tubule to increase excretion of phosphate (phosphaturic effect), regulate vitamin D metabolism, and increase calcium reabsorption. Klotho binds to the TGF-β receptor (TβRII component) to block TGF-β action. Klotho inhibits activation of the inflammatory NF-κB pathway by preventing nuclear translocation of the active form. Klotho increases signaling in the Nrf2 pathway; inducing multiple antioxidant enzymes and inhibiting NF-κB. Klotho blocks IGF-1 receptor signaling; this increases activation of FoxO and antioxidant responses. Klotho also blocks activation of the Wnt pathway by binding to soluble Wnt ligands. Klotho expression is increased by PPAR-γ activation, and also by GLP-1 and GABA stimulation; but is suppressed by angiotensin II activation of the AT1 receptor. Abbreviations: Ang II, angiotensin II; Ca2+, calcium ion; FoxO, forkhead boxprotein O; GABA, γ-aminobutyric acid; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide 1; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor 1; IGFR, IGF-1 receptor; KL, membrane-bound αKlotho; NF-κB, nuclear factor κB; Nrf2, nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2; Pi, inorganic phosphate; PPAR-γ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors γ; R, receptor; sKL, soluble αKlotho; TGF-β, transforming growth factor β; TβRII, TGF-β receptor type II; Vit D, vitamin D.