FIGURE 3.
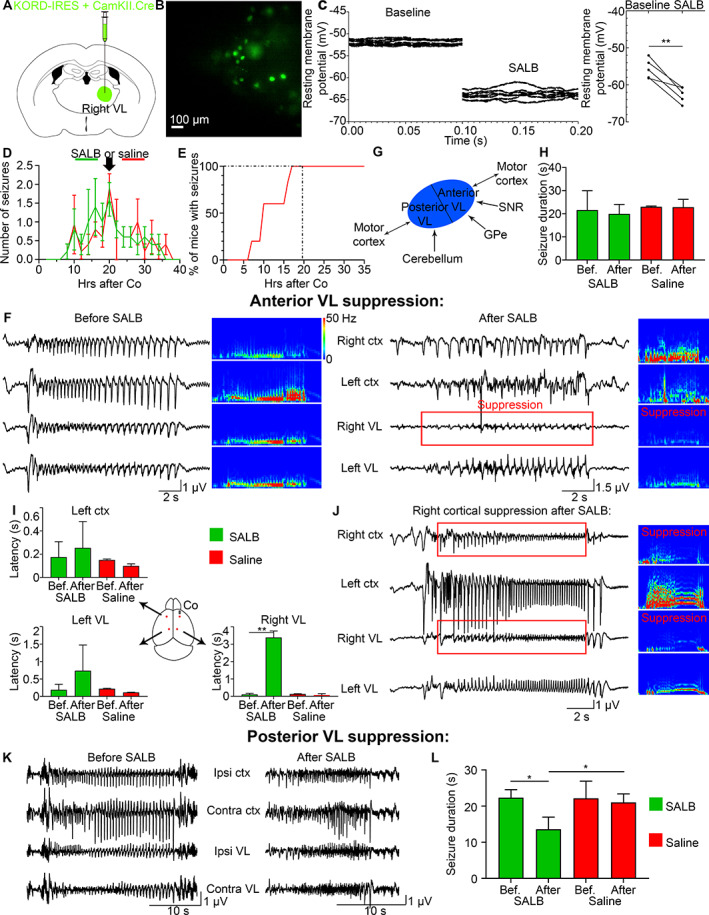
Chemogenetic suppression of the ipsilateral VL does not change the onset latency in the contralateral VL or contralateral cortex. (A) KORD/CamKII.Cre was injected in the right VL. (B) Patch‐clamp recordings were done on KORD‐expressing neurons in the right VL. (C) Resting membrane potential (mV) of transduced cells before and after SALB application, where the left graph is repeated recordings from a single cell, and the right graph is the average for 5 mice. (D) Mean number of seizures in C57Bl/6 mice after cobalt insertion in C57Bl/6 mice that were injected with SALB (green) or saline (red) at 20 hours after Co (black arrow) at the peak of seizures. (E) One hundred percent of all mice developed seizures by 20 hours after Co. (F) LFPs of a seizure recorded before and after SALB injection. Power was suppressed in the right VL (red box). (G) A schematic illustrates anatomical projections to the anterior and posterior VL. (H) Mean seizure duration (seconds) remained the same before (16–20 hours after Co) and after (20–24 hours after Co) SALB or saline injection. (I) Seizure onset was delayed only in the right VL after SALB injection but not in the left cortex or left VL. (J) Right cortex was suppressed after right VL suppression (in 6 out of 11 mice). (K, L) Seizure duration decreased after posterior VL suppression. Co = cobalt; VL = ventrolateral; SALB = salvinorin B.
