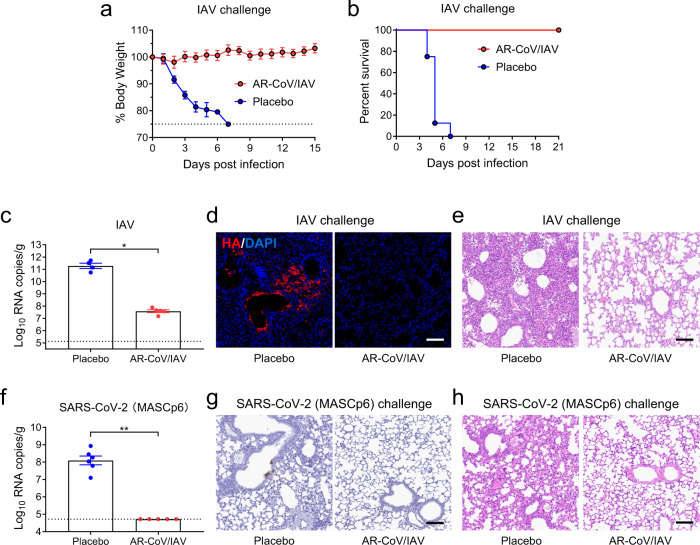
Fig. 4. AR-CoV/IAV protects mice from an IAV or SARS-CoV-2 challenge.
AR-CoV/IAV- or placebo-immunized mice were challenged with 1.5 × 106 PFU of IAV (A/California/07/2009) (a–e) or 1.6 × 104 PFU of SARS-CoV-2 (MASCp6) (f–h) at the indicated time points post-initial immunization. a Weight changes were recorded for 15 days and are shown as the mean ± SEM (AR-CoV/IAV, n = 7; placebo, n = 8). b Mortality was monitored for 21 days after inoculation. c Viral RNA copies in the lung tissues of IAV-infected mice (AR-CoV/IAV, n = 5; placebo, n = 4) were determined by qRT–PCR and are shown as the mean ± SEM. d Immunostaining results for HA protein in lung tissues. e H&E staining of lung tissues from IAV-infected mice. f Viral RNA copies in the lung tissues of SARS-CoV-2-infected mice (AR-CoV/IAV, n = 5; placebo, n = 6) were determined by qRT–PCR and are shown as the mean ± SEM. g ISH assay of lung tissues from SARS-CoV-2-infected mice. h H&E staining of lung tissues from SARS-CoV-2-infected mice. Scale bar, 100 μm. Statistical differences between groups were analyzed using two-tailed unpaired t tests. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.