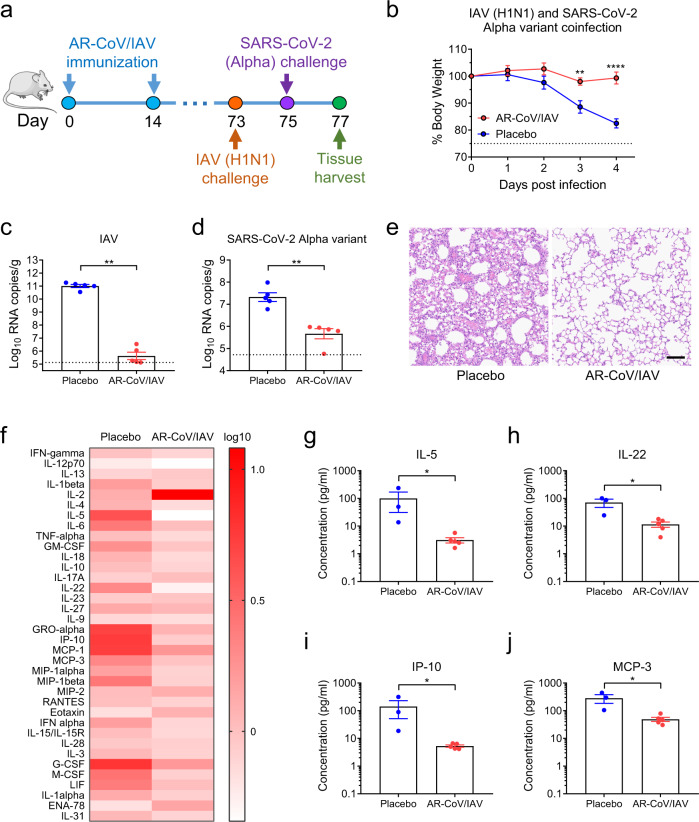
Fig. 5. AR-CoV/IAV confers protection against coinfection with IAV and the SARS-CoV-2 Alpha variant in mice.
a Schematic diagram of experimental design. Groups of AR-CoV/IAV- or placebo-immunized mice were intranasally challenged with 2 × 105 PFU of IAV (A/California/07/2009) 73 days after the initial immunization, followed by infection with 4 × 103 PFU of the SARS-CoV-2 Alpha variant 2 days later. Mice were sacrificed 4 days after IAV infection for viral detection and histopathological analysis. b Weight changes in infected mice (n = 5) were recorded for 4 days post-infection and are shown as the mean ± SEM. c, d Viral RNA copies of IAV (c) and SARS-CoV-2 (d) in the lung tissues of infected mice (n = 5) were determined by qRT–PCR and are shown as the mean ± SEM. e Histopathologic analysis of lung sections from coinfected mice. Scale bar, 100 μm. f Serum cytokine and chemokine analyses were determined by Luminex and are presented as fold changes compared to samples collected before infection (AR-CoV/IAV, n = 5; placebo, n = 3). g–j Concentrations of cytokines and chemokines in serum samples collected post-infection. Data are shown as the mean ± SEM. Statistical differences were analyzed by using two-way ANOVA with multiple comparison tests or two-tailed unpaired t tests. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001.