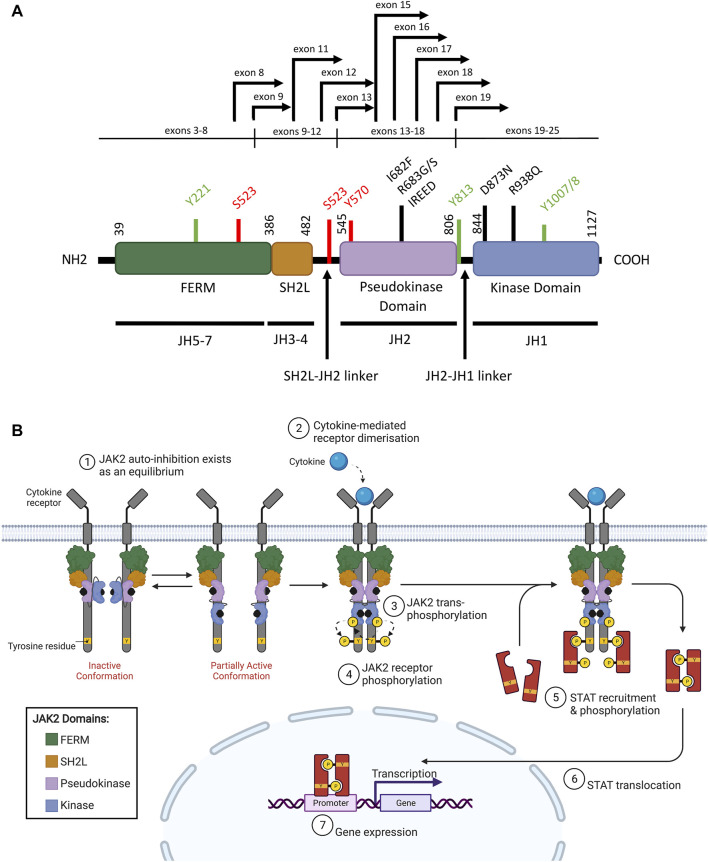
FIGURE 2.
WT JAK2 structure and function (A) Schematic representation of the JAK2 domain structure (NCBI reference sequence: NP_004963.1) encoded by the seven JAK homology (JH) domains. The FERM (4.1 protein, ezrin, radixin, moesin), SH2 (Src homology 2)-like (SH2L), pseudokinase (JH2) and kinase (JH1) domains are represented by purple, red, light blue, and dark blue respectively. Key residues for phosphorylation for positive (green) or negative (red) regulation are shown. Mutations commonly associated with ALL (black lines) and JAK2 fusion breakpoints (black arrows) are indicated. Adapted from Silvennoinen and Hubbard (2015b) (Silvennoinen and Hubbard, 2015a). (B) Schematic representation of JAK/STAT signaling pathway activation through JAK2. The JAK2 FERM and SH2L domains associate with the cytoplasmic juxtamembrane motifs of a cytokine receptor (grey) to recruit JAK2 to the cell membrane. The four domains of JAK2 are presented: FERM (green), SH2-like (orange), pseudokinase (JH2, purple), and kinase (JH1, blue). JAK2 is shown bound to ATP (black). The proposed model of JAK2 activation suggests that JAK2 exists in an equilibrium between inactive and partially active conformations. In the inactive conformation (left), the JAK2 kinase domain is inhibited by a JH2-mediated autoinhibitory interaction. In the partially active conformation (right), the JAK2 kinase domain is released from the JH2-mediated auto-inhibition and is available for some limited transphosphorylation. Cytokine (cyan) binding to their cognate receptor promotes receptor dimerisation, which facilitates JAK2 activation by transphosphorylation (arrows). JAK2 then auto-phosphorylates the cytoplasmic region of the receptor creating recruitment sites for cytoplasmic STATs (red). JAK2-mediated STAT phosphorylation facilitates STAT dimerisation. These STAT dimers are then translocated to the nucleus where they regulate gene expression by binding to promoters with STAT-binding sites. Adapted from Hubbard (2018) and “Cytokine Signaling through the JAK-STAT Pathway” (BioRender.com, 2021).