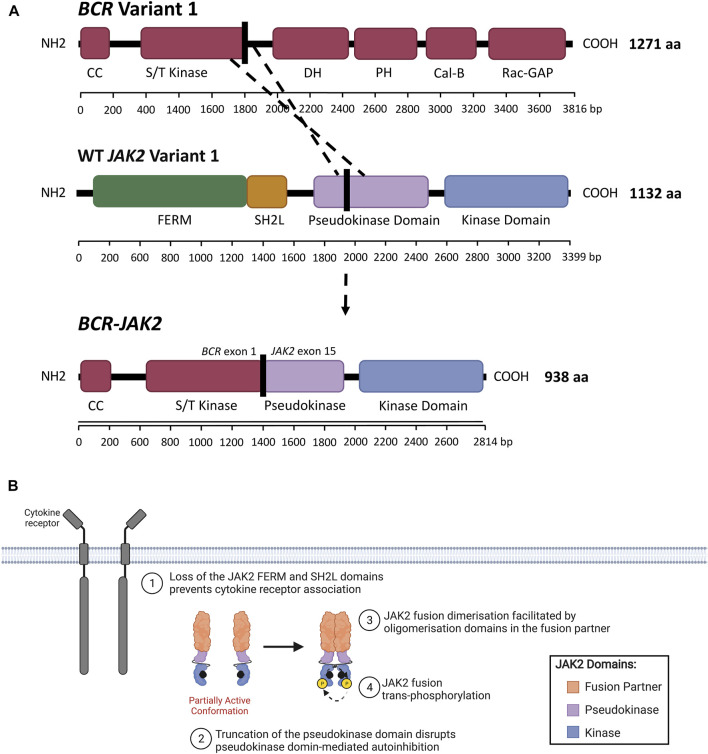
FIGURE 5.
JAK2 fusion proteins in ALL. (A) Schematic representation of a genomic rearrangement between JAK2 exon 15 and BCR exon 1 that produces the BCR-JAK2 fusion gene. BCR isoform 1 (encoded by BCR variant 1) contains the following domains: BCR coiled-coil (CC), serine/threonine kinase (S/T kinase), DH (Dbl homology), PH (pleckstrin homology), Cal-B (calcium-dependent lipid-binding) and Rac-GAP (Rac GTPase-activating protein) domains. The BCR DH and PH domains form the Rho-GEF domain (Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor). JAK2 isoform A (encoded by JAK2 variant 1) contains FERM (4.1 protein, ezrin, radixin, moesin), SH2-like (SH2L, Src homology 2), pseudokinase (JH2) and kinase (JH1) domains. The BCR-JAK2 fusion protein retains the BCR CC and S/T kinase domains, three exons of the JAK2 pseudokinase domain and the full-length JAK2 kinase domain. BCR-JAK2 is predicted to homodimerise via its retained BCR CC motif. Domains encoded by the BCR, JAK2 and BCR-JAK2 transcripts were annotated using InterPro (EMBL-EBI, 2021) (Jones et al., 2014; Blum et al., 2021) and Maru amd Witte (1991). (B) Schematic representation of JAK/STAT signaling pathway activation through JAK2 fusions. All JAK2 fusions comprise of an N-terminal fusion partner (orange) and the full-length JAK2 kinase domain (JH1, blue). The full-length or truncated JAK2 pseudokinase domain (JH2, purple) may also be present or absent in different JAK2 fusions. The absence of the JAK2 FERM and SH2-like domains prevent JAK2 fusions from associating with the cytoplasmic juxtamembrane motifs of cytokine receptors (dark grey). JAK2 fusions are shown bound to ATP (black). The proposed model of JAK2 fusion activation suggests that oligomerization domains within the fusion partner may facilitate JAK2 fusion dimerisation and subsequent trans-phosphorylation, promoting malignant transformation. Adapted from “Cytokine Signaling through the JAK-STAT Pathway” (BioRender.com, 2021).