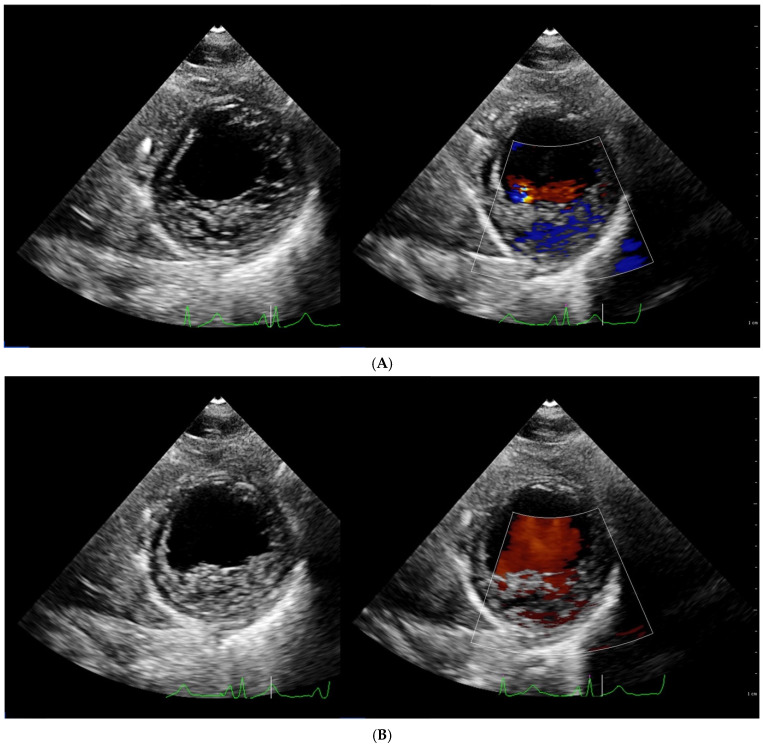
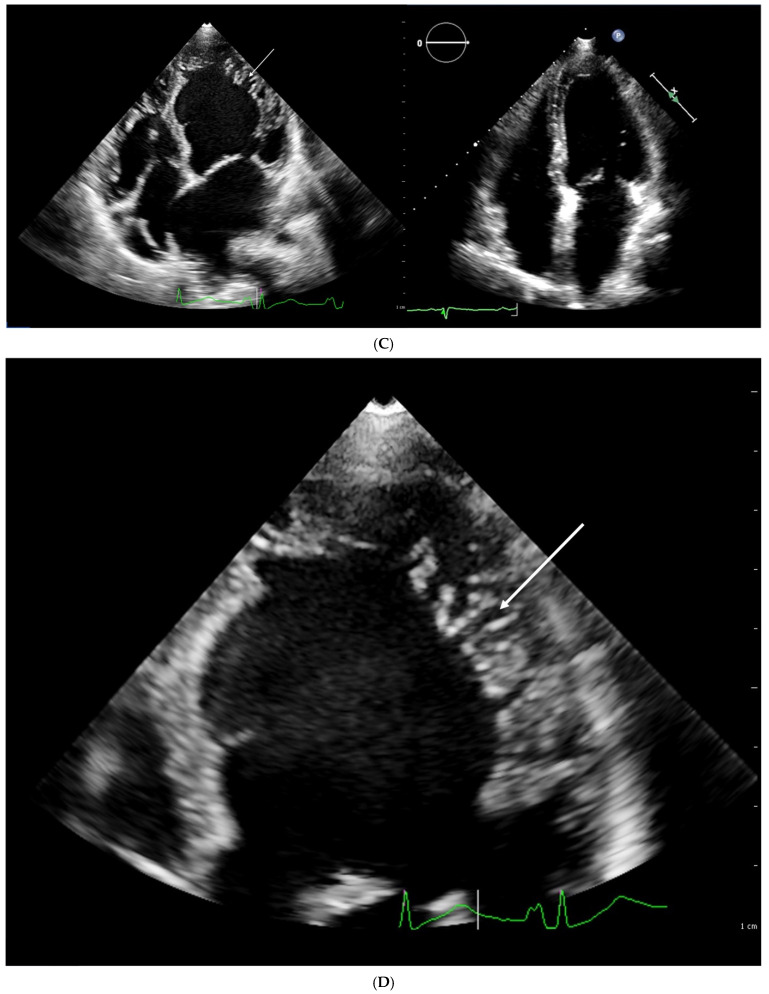
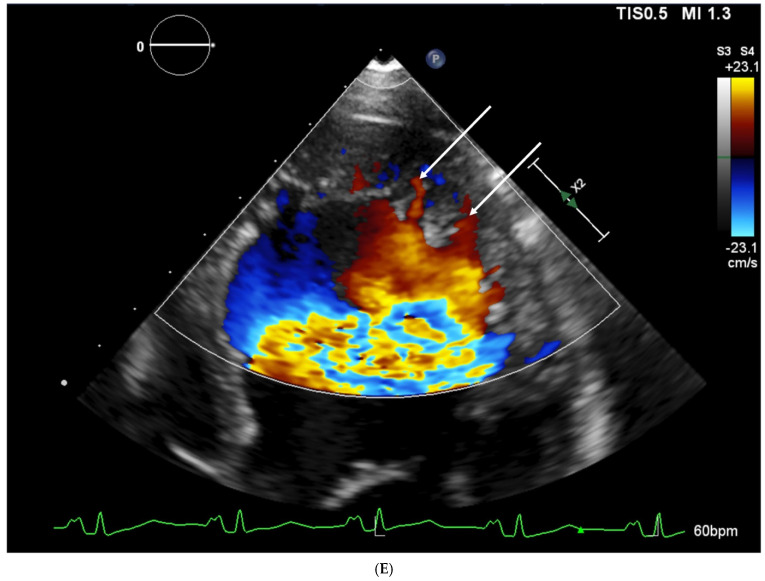
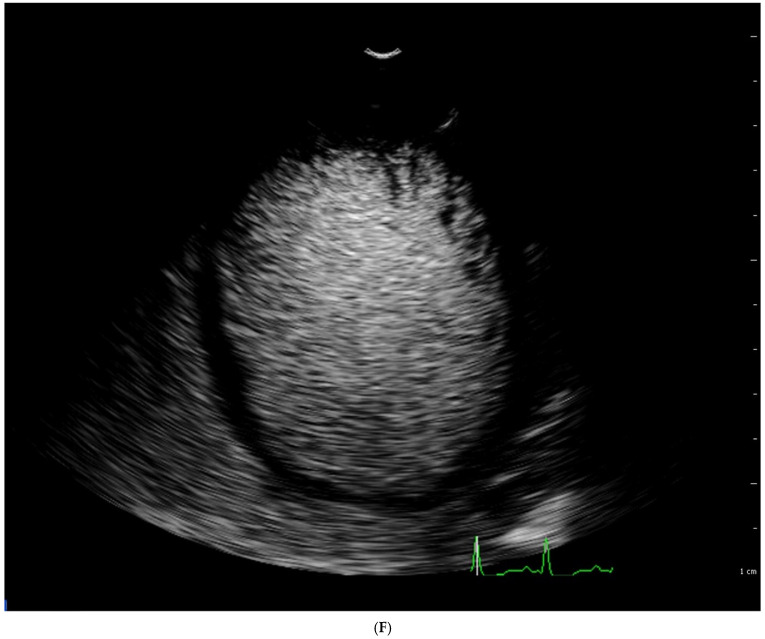
Figure 1.
Transthoracic echocardiographic examination, patient with LVNC. (A) Parasternal short axis, 2D, diastole, right with color doppler. (B) Parasternal short axis, 2D, systole, right with color doppler. (C) Apical 4-chamber view, 2D, diastole. Left—note excessive trabeculation of the left ventricle. The white arrow shows the deep trabecular recess between the trabeculation. Right—healthy patient with a normal left ventricle. (D) Zoomed view of the same patient, apex, and apical segments of the lateral wall. Note excessive trabeculation of the left ventricle. The white arrow shows the deep trabecular recess between the trabeculation. (E) Zoomed view with color doppler of the same patient, apex, and apical segments of the lateral wall. Note excessive trabeculation of the left ventricle filled with blood as seen with color doppler (arrows). (F) Contrast echocardiography (SonoVue), modified apical 4 chamber view, end-diastole, patient with LVNC. Note the deep trabecular recess between trabeculation of the left ventricle filled with contrasted blood.