Fig. 1 |. snRNA-seq and immunohistological analyses of imGCs in the human infant hippocampus.
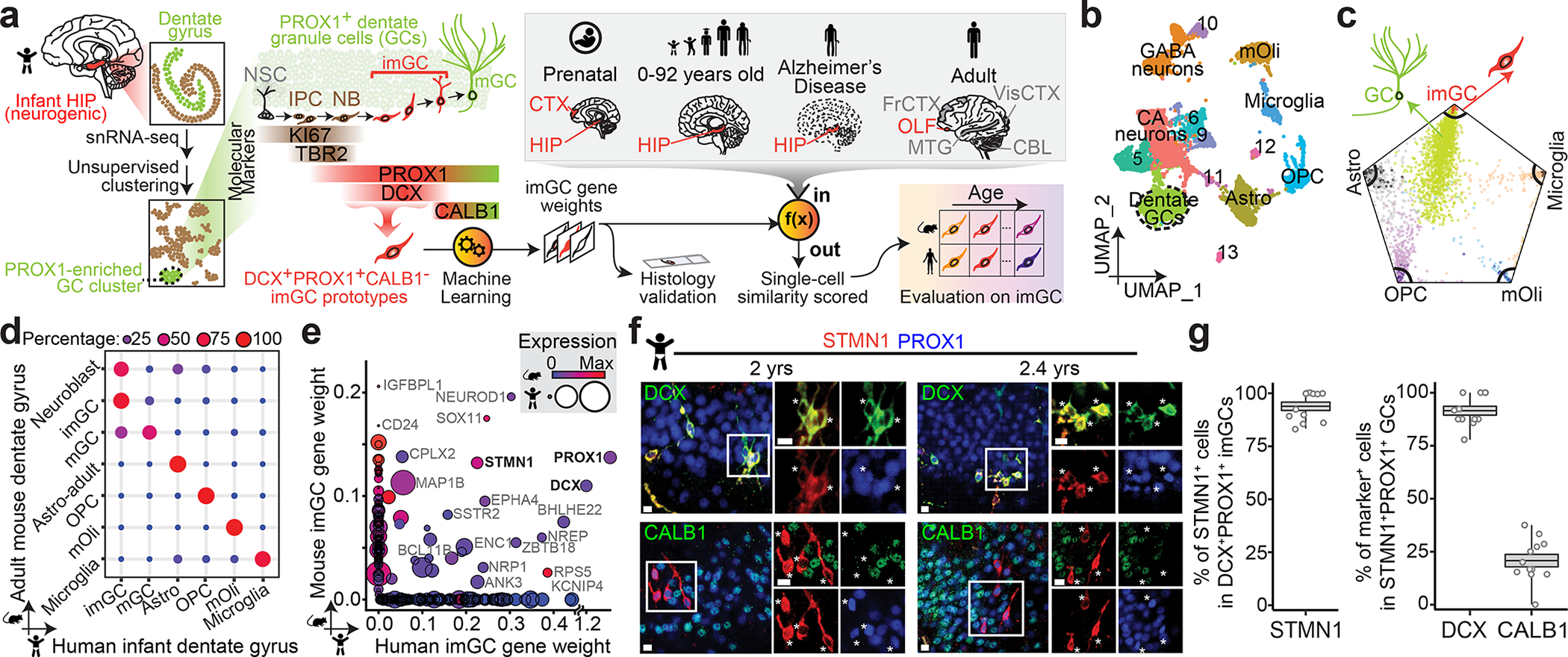
a, A schematic illustration of the experimental design. HIP: hippocampus; NSC: neural stem cell; IPC: intermediate neural progenitor cell; NB: neuroblast; imGC: immature granule cell; mGC: mature granule cell; CTX: cortex; OLF: olfactory epithelium; FrCTX: frontal cortex; VisCTX: visual cortex; CBL: cerebellum; MTG: middle temporal gyrus of cortex. b, UMAP visualization of 15,434 nuclei from four human infant hippocampal specimens, colored by cluster. The GC cluster is highlighted with a dashed line cicle. mOli: mature oligodendrocyte; OPC: oligodendrocyte precursor cell; Astro: astrocyte. c, Wheel plot visualizing scores of each cell to each prototype by the machine learning model. Dots represent individual cells whose distance to each prototype is proportional to the similarity score of that prototype. Each black line indicates a similarity score of 0.85 to each prototypical cell type. d, Transcriptional congruence between the corresponding mouse9 and human cell types measured by a multi-class random forest classifier24,32 trained on different human cell types. Confusion matrix plot indicates the percentage of cells of a given mouse cell cluster (row, based on published annotations9) assigned to a corresponding human cell type (column, classified by the machine learning model). e, Comparison of positive gene weights defining imGCs in humans and mice generated by separate machine learning models. f, g, Sample confocal immunostaining images (f) and quantification (g) of STMN1 enrichment in imGCs in the human infant hippocampus. Scale bars, 10 μm. Asterisks indicate DCX+ or CALB1− among STMN1+PROX1+ cells (f). Dots represent data from individual sections and box values represent mean ± s.e.m. with whiskers for max and min (n = 4 subjects) (g).
