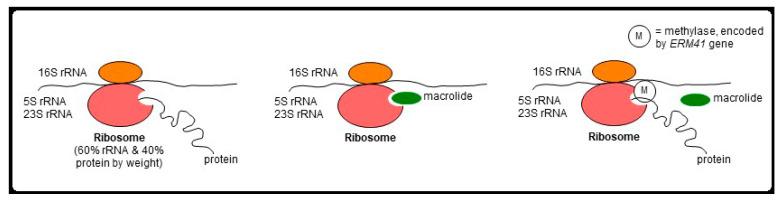
Figure 4.
Mechanism of inducible resistance in M. abscessus. In M. abscessus sensu stricto and M. bolletii, macrolide binds to 23S rRNA and inhibits bacterial protein synthesis. With induction of methylase production by clarithromycin, the methylase prevents the binding of macrolide, creating an inducible resistance. Since clarithromycin induction of the ERM41 gene to produce methylase is much greater than by azithromycin, clarithromycin is much more likely to induce macrolide resistance than azithromycin.