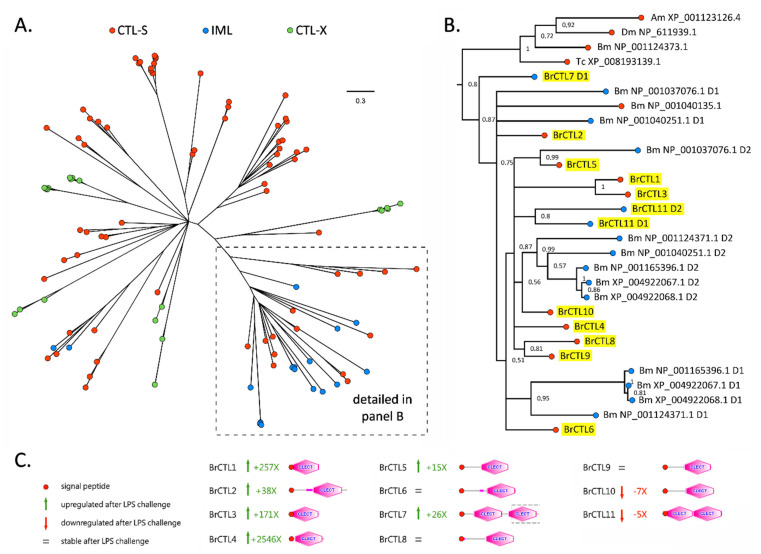
Figure 2.
Bayesian phylogeny of insect CTL domain-containing proteins, including representatives from Drosophila melanogaster (Diptera), Tribolium castaneum (Coleoptera), Apis mellifera (Hymenoptera), and Bombyx mori (Lepidoptera), plus the 11 CTLs identified in B. rossius. The full unrooted tree, which depicts the complex evolutionary relationships among the three major structural classes of CTLs (i.e., CTL−S, IML, and CTL−X) is displayed in panel (A). The branch that includes all B. rossius CTLs (highlighted with a yellow background) are detailed in panel (B). The numbers shown close to each node represent posterior probability support values. Poorly supported nodes (i.e., <0.5) were collapsed. Dm: D. melanogaster; Am: A. mellifera; Tc: T. castaneum; Bm: B. mori. Panel (C) reports the domain architectures and gene expression trends following LPS stimulation of B. rossius CTLs. The portion of BrCTL7 included in a dashed box indicates a missing, unassembled region. D1 and D2 indicate the two CLECT domains of IMLs.