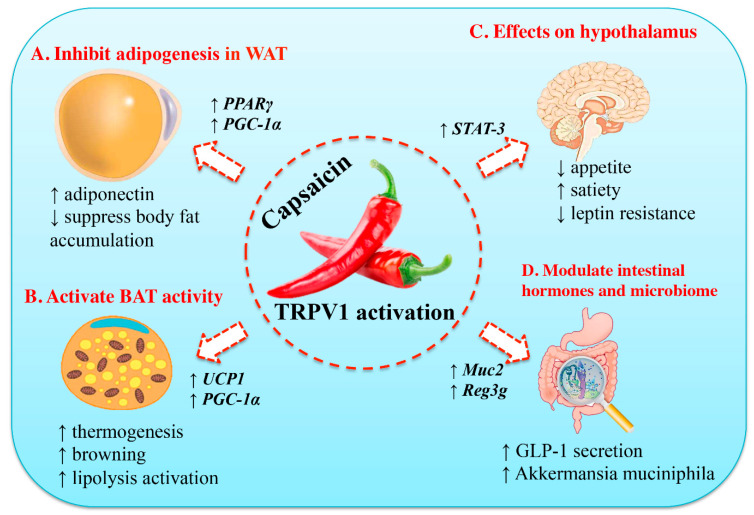
Figure 2.
Molecular mechanisms of the anti-obesity effects of capsaicin. (A) Capsaicin can inhibit adipogenesis in preadipocyte and adipocyte by up-regulating the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) and uncoupling protein-1 (UCP-1). Thus, it will stimulate adiponectin secretion and increase body fat accumulation. (B) Capsaicin can activate brown adipose tissue (BAT) activity, accompanied by increased expression of UCP-1 and PPAR-coactivator-1α (PGC-1α). (C) Capsaicin can suppress appetite, increase satiety, and ameliorate insulin resistance. (D) Capsaicin can modulate its function in the gastrointestinal tract and gut microbiome, including stimulation of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) secretion and increase in population of the gut bacterium Akkermansia muciniphila. STAT-3, and signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 (STAT3). Reproduced with permission from [66].