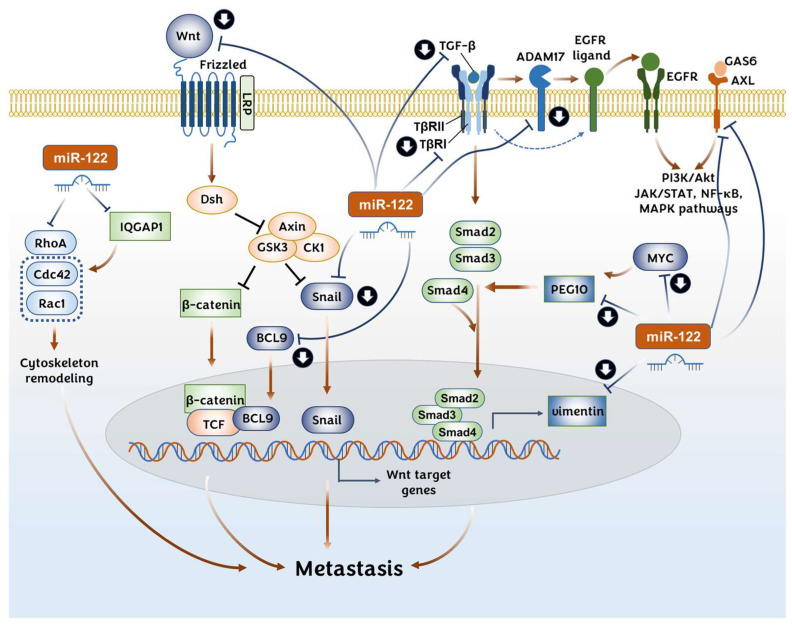
Figure 4.
Regulation of metastasis of cancer cells by miR-122. Without any external stimulation, β-catenin is phosphorylated by the degradation complex kinases, comprising glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3) and casein kinase 1α (CK1α). This leads to the degradation of β-catenin by the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway. The binding of the Wnt protein to the Frizzled receptor and co-receptors, such as the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5) or LRP6, initiates the dissociation of the degradation complex kinases, thereby stabilizing β-catenin and leading to the expression of Wnt target genes. miR-122 can downregulate the expression of WNT, BCL9, and vimentin, leading to the loss of their metastatic ability. The TGF-β signaling suppresses apoptosis and promotes EMT at the later stages of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) development. The activation of TGF-β transduces a signal through Smad proteins. Also, PEG10 regulates TGF-β signaling positively in HCC. miR-122 downregulates the expression of TGF-β, TβRI, and PEG10. TGF-β signaling can also enhance the EGFR signaling by activating ADAM17. Signaling by the AXL receptor, another target of miR-122, also contributes to the metastasis of HCC by activating PI3k/Akt, JAK/STAT, NF-κB, and MAPK pathways.