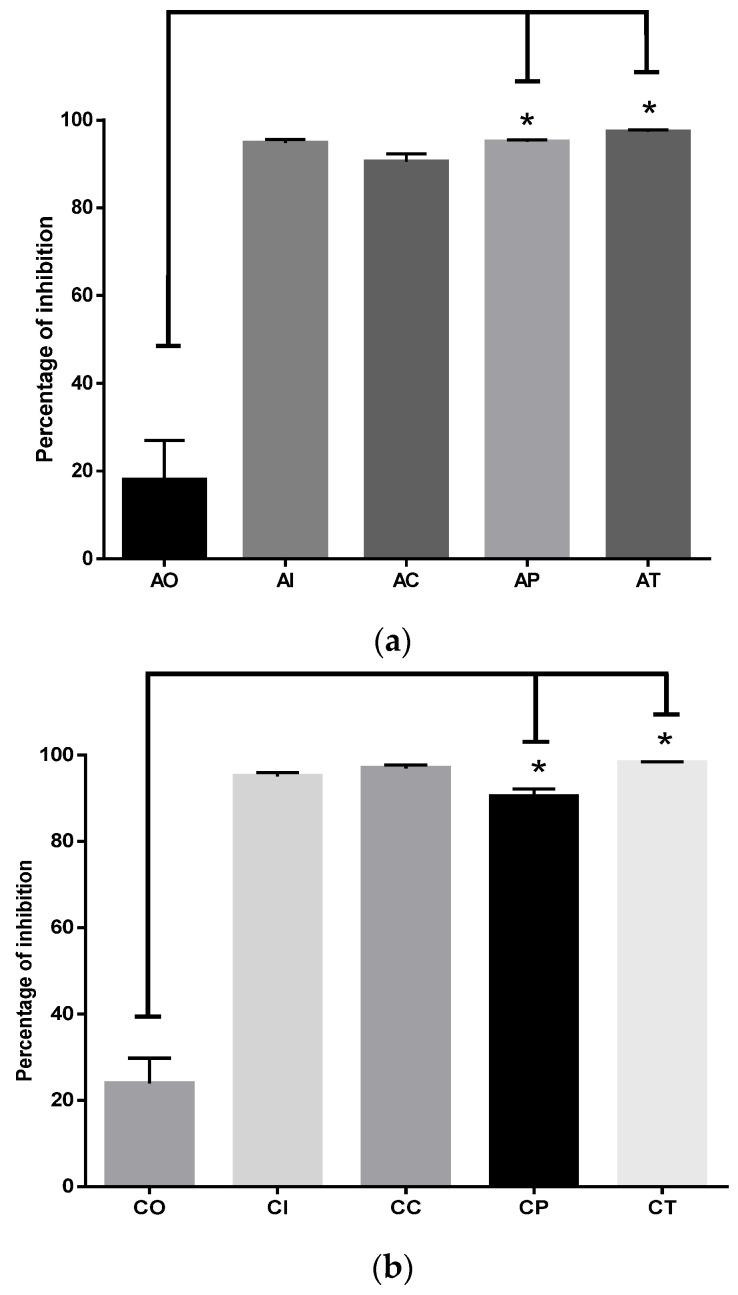
Figure 4.
Inhibition of oxidative damage to lipids by curcumin in acute and chronic phases after exposure to ozone: (a) in the acute exposure to ozone, the administration of dietary curcumin in preventive and therapeutic modes significantly inhibited the oxidative damage to lipids (* p < 0.01) compared to the control group exposed to ozone OA; acute O3 (AO), acute intact (AI), acute CUR (AC), acute preventive (AP), acute therapeutic (AT); (b) the effect of curcumin in preventive and therapeutic administration significantly inhibited oxidative damage to lipids (* p < 0.01), compared to the CO group; chronic O3 (CO), chronic intact (CI), chronic CUR (CC), chronic preventive (CP), chronic therapeutic (CT).